I1- ISIS level 1, I2- ISIS level2,
I- route type intra, IA- route type inter, E- route type external,
i- metric type internal, e- metric type external,
O- OSPF, E1- external type 1, E2- external type2,
N1- NSSA external type1, N2- NSSA external type2
Prefix/Length Type Next Hop Dist/Met Intf
------------------ ------- --------------- -------------- ------------
10.100.3.3/32 Bgp 10.12.12.1 33/44 ATM5/1.12
10.63.42.23/32 Bgp 10.45.2.31 33/44 ATM5/1.14
Access Lists
An access list is a sequential collection of permit and deny conditions that you can
use to filter inbound or outbound routes. You can use different kinds of access lists
to filter routes based on either the prefix or the AS path.
Filtering Prefixes
To filter routes based on the prefix, you can do any of the following:
■
Define an access list with the
access list
command and apply the list to routes
received from or passed to a neighbor with the
neighbor distribute-list
command.
■
Define a prefix list with the
ip prefix-list
command and apply the list to routes
received from or passed to a neighbor with the
neighbor prefix-list
command.
■
Define a prefix tree with the
ip prefix-tree
command and apply the list to routes
received from or passed to a neighbor with the
neighbor prefix-tree
command.
The router compares each route’s prefix against the conditions in the list or tree one
by one. If the first match is for a permit condition, the route is accepted or passed.
If the first match is for a deny condition, the route is rejected or blocked. The order
of conditions is critical because testing stops with the first match. If no conditions
match, the router rejects or blocks the address; that is, the last action of any list is
an implicit deny condition for all routes. The implicit rule is displayed by
show
access-list
and
show configuration
commands.
You cannot selectively place conditions in or remove conditions from an access list,
prefix, list, or prefix tree. You can insert a new condition only at the end of a list or
tree.
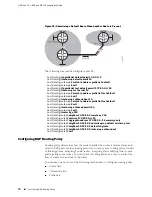
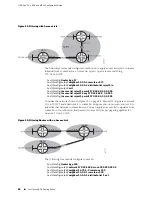
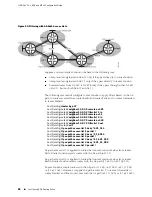
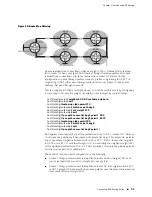
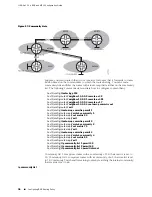
Consider the network structure in Figure 21 on page 84.
Configuring BGP Routing Policy
■
83
Chapter 1: Configuring BGP Routing
Summary of Contents for BGP
Page 6: ...vi ...
Page 8: ...viii JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 37: ...Part 1 Border Gateway Protocol Configuring BGP Routing on page 3 Border Gateway Protocol 1 ...
Page 38: ...2 Border Gateway Protocol JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 234: ...198 Monitoring BGP JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 236: ...200 Multiprotocol Layer Switching JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 542: ...506 Monitoring BGP MPLS VPNs JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 544: ...508 Layer 2 Services Over MPLS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 610: ...574 Virtual Private LAN Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 624: ...588 VPLS References JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 680: ...644 Virtual Private Wire Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 724: ...688 Monitoring MPLS Forwarding Table for VPWS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 725: ...Part 6 Index Index on page 691 Index 689 ...
Page 726: ...690 Index JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...