■
Use to assign a VRF to an interface or subinterface by forwarding the interface
from the VR to the VRF. This command also enables you to specify secondary
routing table lookup for a VRF if an initial routing table lookup is unsuccessful.
■
Forwarding the interface removes the IP configuration from the interface. You
must reassign an IP address to the interface after you issue this command.
■
The
ip vrf forwarding
command changes the prompt to indicate that the CLI is
now in Interface Configuration mode within the child VRF. This condition persists
only for as long as you are configuring attributes on the given interface within
the VRF. Entering a top-level command, such as
interface
, within this VRF context
takes the CLI out of the VRF context back to the parent VR context.
■
When you issue the
ip vrf forwarding
command from within the Interface
Configuration or Subinterface Configuration mode of the parent VR, the IP address
and other attributes of the interface are deleted from the interface. You must
then reconfigure the IP attributes in the context of the VRF after issuing the
command.
■
Example
host1:vr1(config-if)#
ip vrf forwarding vrfA
host1:vr1:vrfA(config-if)#
ip address 10.12.4.5 255.255.255.0
or
host1:vr1(config-if)#
ip vrf forwarding vrfA fallback global
host1:vr1:vrfA(config-if)#
ip address 10.12.4.5 255.255.255.0
■
Use the
no
version to remove the interface assignment or discontinue secondary
routing table lookup.
■
See ip vrf forwarding.
Adding Static Routes to a VRF
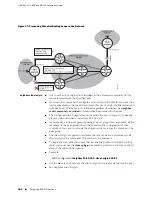
Consider the network structure shown in Figure 92 on page 436. If no routing
protocol—BGP or any other IGP—is running between the PE router and the CE router,
you must use the
ip route vrf
command to add a static route in the customer's VRF
for each prefix in that customer's site.
Each of these static routes must point to the link connecting the PE router to the CE
router. Typically, you redistribute these static routes in the VRF's address family in
BGP or use
network
commands to make those prefixes reachable from other CE
routers in the same VPN.
Configuring BGP VPN Services
■
435
Chapter 5: Configuring BGP-MPLS Applications
Summary of Contents for BGP
Page 6: ...vi ...
Page 8: ...viii JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 37: ...Part 1 Border Gateway Protocol Configuring BGP Routing on page 3 Border Gateway Protocol 1 ...
Page 38: ...2 Border Gateway Protocol JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 234: ...198 Monitoring BGP JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 236: ...200 Multiprotocol Layer Switching JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 542: ...506 Monitoring BGP MPLS VPNs JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 544: ...508 Layer 2 Services Over MPLS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 610: ...574 Virtual Private LAN Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 624: ...588 VPLS References JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 680: ...644 Virtual Private Wire Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 724: ...688 Monitoring MPLS Forwarding Table for VPWS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 725: ...Part 6 Index Index on page 691 Index 689 ...
Page 726: ...690 Index JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...