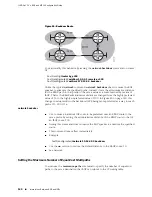
You must configure a cluster ID, because router Acton and router Harvard are both
route reflectors in this cluster.
To configure router Harvard as a route reflector:
host4(config)#
router bgp 29
host4(config)#
bgp cluster-id 23
host4(config-router)#
neighbor 10.3.1.2 remote-as 29
host4(config-router)#
neighbor 10.3.1.2 route-reflector-client
host4(config-router)#
neighbor 10.1.2.1 remote-as 29
host4(config-router)#
neighbor 10.1.2.1 route-reflector-client
host4(config-router)#
neighbor 10.3.3.2 remote-as 29
host4(config-router)#
neighbor 10.2.5.2 remote-as 29
You must configure a cluster ID, because router Harvard and router Acton are both
route reflectors in this cluster.
bgp client-to-client reflection
■
Use to reenable the reflector to reflect routes among all clients.
■
Client-to-client reflection is enabled by default. If the route reflector’s clients are
fully meshed, you can disable reflection because it is not necessary.
■
If client-to-client reflection is enabled (the default), clients of a route reflector
cannot be members of a peer group.
■
Example
host1(config-router)#
no bgp client-to-client reflection
■
Changes apply automatically to any routes received after you issue the command.
To advertise or withdraw routes that are already present in the BGP routing table,
you must use the
clear ip bgp
command to issue a hard clear or an outbound
soft clear.
■
Use the
no
version to disable route reflection; use only if the route reflector’s
clients are fully meshed.
■
See bgp client-to-client reflection.
bgp cluster-id
■
Use to configure a cluster ID on the route reflectors if the BGP cluster has more
than one route reflector. For clusters with a single reflector, the cluster ID is the
reflector’s router ID and does not have to be configured.
■
You specify a cluster ID number or an IP address of a router acting as a route
reflector.
■
The new cluster ID is used in update messages sent after you issue the command.
To force BGP to resend all routes with the new cluster ID, you must use the
clear
ip bgp
command to perform a hard clear or a soft clear.
■
Use the
no
version to cause BGP to use the router ID as the cluster ID.
■
See bgp cluster-id.
neighbor route-reflector-client
152
■
Managing a Large-Scale AS
JUNOSe 11.1.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide
Summary of Contents for BGP
Page 6: ...vi ...
Page 8: ...viii JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 37: ...Part 1 Border Gateway Protocol Configuring BGP Routing on page 3 Border Gateway Protocol 1 ...
Page 38: ...2 Border Gateway Protocol JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 234: ...198 Monitoring BGP JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 236: ...200 Multiprotocol Layer Switching JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 542: ...506 Monitoring BGP MPLS VPNs JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 544: ...508 Layer 2 Services Over MPLS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 610: ...574 Virtual Private LAN Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 624: ...588 VPLS References JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 680: ...644 Virtual Private Wire Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 724: ...688 Monitoring MPLS Forwarding Table for VPWS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Page 725: ...Part 6 Index Index on page 691 Index 689 ...
Page 726: ...690 Index JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...