SNMP Configuration
281
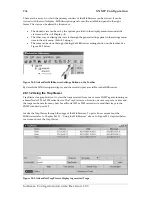
Example: Setting Access Community Information
In the following example the SNMP communities for the default community public with read-only
access and the undisclosed community
Not4evEryOne
with read/write access are defined. Only these
valid communities have access to the information from the SNMP agent running on the respective
SmartNode 1000 or 2000 series device.
SN2300-01(cfg)#
snmp community public ro
SN2300-01(cfg)#
snmp community Not4evEryOne rw
Note:
If no community is set on your SmartNode accessing any of the MIB objects is not possible!
28.8 Setting Allowed Host Information
If a host has to access SNMP MIB objects on a certain node it explicitly needs the right to access the
SNMP agent on the respective SmartNode 1000 or 2000 series device. Therefore a host needs an entry
on a SmartNode 1000 or 2000 series device, which allows accessing the device. The host is identified
by its IP address and has to use a certain community string for security precautions.
Note:
the community which is to be used as security name to access the MIB objects has to be defined
prior to the definition of allowed hosts.
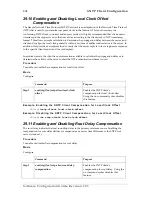
Procedure
Adding a host that is allowed to access the MIB of this system
Mode
Configure
Command
Purpose
Step 1
node
(cfg)#snmp host
IP-address-of-node
security-name
community
Configures a host that with IP address
IP-address-of-node
can access the MIB of
this SmartNode 1000 or 2000 series
device, using the security name
community
.
Use the
no
command option to remove a SNMP allowed host setting.
Example: Setting Allow ed Host Information
In the following example the host with IP address
172.16.224.45
shall be able to access the MIB of this
SmartNode 2000 series device using community
public
as security name.
SN2300-01(cfg)#
snmp host 172.16.224.45 security-name public
28.9 Specifying The Default SNMP Trap Target
An SNMP trap is a message that the SNMP agent running on a SmartNode 1000 or 2000 series device
sends to a network management station. For example, an SNMP agent would send a trap when an
interface's status has changed from up to down. The SNMP agent must know the address of the
network management station so that it knows where to send traps. It is possible to define more than
one SNMP trap target.
The SNMP message header contains a
community
field. The SNMP agent running on a SmartNode
1000 or 2000 series device uses a defined community name, which is inserted in the trap messages
Software Configuration Guide, Revision 1.03
Summary of Contents for SmartWare R2.00
Page 2: ......