Gateway Configuration
239
25 GATEWAY CONFIGURATION
This chapter provides an overview of ISoIP and H.323 gateways and describes the tasks involved in
configuring them. For detailed information on command syntax and usage guidelines for the
commands listed in the configuration tasks refer to Chapter 20, “Gateway ISoIP Mode”, and Chapter
21, “Gateway H.323 Mode” in the SmartWare
Command Reference Guide.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•
Introduction
•
Gateway Configuration Tasks
•
Examples
25.1 Introduction
When communication is required between different networks a gateway is always needed between
them. A gateway provides:
•
Data format translation, e.g. audio and video CODEC translation
•
Control signalling translation, e.g call setup and termination functionality on both sides of a
network.
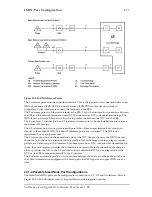
In the case of SmartWare, a gateway connects two contexts of different types, for example the CS and
the IP context. It handles connections between different technologies or protocols and contains
general gateway configuration parameters. In SmartWare there is an ISoIP and an H.323 gateway.
The ISoIP and H.323 interfaces in the CS context are implicitly bound to these gateways. The H.323
gateway must be bound explicitly to interfaces in the IP context. The ISoIP gateway detects the
correct IP interface on the IP context for its call automatically, therefore no binding is needed. Figure
25-1 illustrates the function of the gateways. SmartWare currently supports one instance of each
gateway. The name of the H.323 gateway is
h323
and the one for the ISoIP gateway is
isoip
.
Software Configuration Guide, Revision 1.03
Summary of Contents for SmartWare R2.00
Page 2: ......