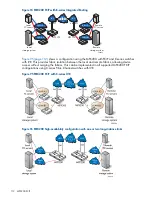
•
Initiator
:
Multiple NIC/iSCSI HBA ports—four recommended
◦
–
one public
–
one private
–
two storage, for higher availability and performance
◦
MPIO - use HP DSM or the Microsoft Generic DSM
–
HP recommends using the latest available
•
Connectivity
: Dual blade configuration for redundancy
Setting up authentication
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) is an authentication protocol used for secure
login between the iSCSI initiator and iSCSI target. CHAP uses a challenge-response security
mechanism to verify the identity of an initiator without revealing the secret password shared by
the two entities. It is also referred to as a three-way handshake. With CHAP, the initiator must
prove to the target that it knows the shared secret without actually revealing the secret. You can
configure CHAP on the MPX200.
NOTE:
Setting up authentication for your iSCSI devices is optional. If you require authentication,
HP recommends that you configure it after you have properly verified installation and operation
of the iSCSI implementation without authentication.
In a secure environment, authentication may not be required—access to targets is limited to trusted
initiators. In a less secure environment, the target cannot determine if a connection request is from
a certain host. In this case, the target can use CHAP to authenticate an initiator.
When an initiator contacts a target that uses CHAP, the target (called the authenticator) responds
by sending the initiator a challenge. The challenge consists of information that is unique to the
authentication session. The initiator encrypts this information using a previously issued password
that is shared by both the initiator and the target. The encrypted information is then returned to the
target. The target has the same password and uses it as a key to encrypt the information that it
originally sent to the initiator. The target compares its results with the encrypted results sent by the
initiator; if they are the same, the initiator is considered authentic. These steps are repeated
throughout the authentication session to verify that the correct initiator is still connected.
These schemes are called proof-of-possession protocols. The challenge requires that an entity prove
possession of a shared key or one of the key pairs in a public-key scheme.
See the following RFCs for detailed information about CHAP:
•
RFC 1994 (PPP Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol, August 1996)
•
RFC 2433 (Microsoft PPP CHAP Extensions, October 1998)
•
RFC 2759 (Microsoft PPP CHAP Extensions version 2, January 2000)
General CHAP restrictions
The CHAP restrictions are:
•
Maximum length of 100 characters
•
Minimum length of 1 character
•
Entering an IQN using the HP P6000 Command View add host tab requires the iSCSI initiator
to have been registered in the iSCSI or iSCSI/FCoE module's initiator database.
Setting up authentication
97