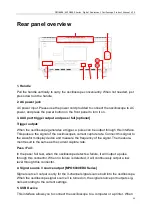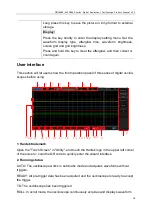
DPO6000, MPO6000 Series Digital Fluorescent Oscilloscope Product Manual V1.3
21
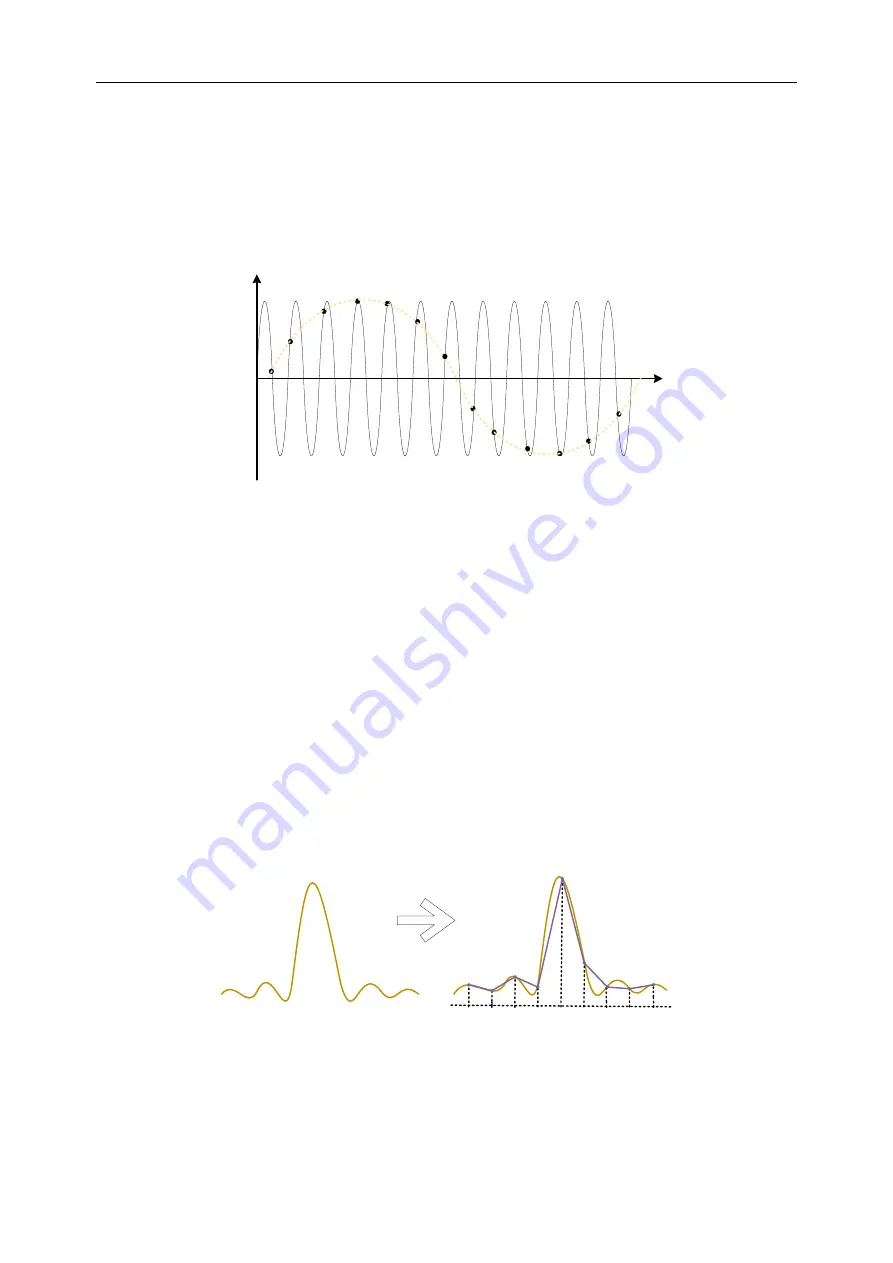
Waveform aliasing
If the sampling cannot be satisfied (Fs> 2Fmax), the waveform frequency when recon-
structing the sampled data is smaller than the frequency of the actual signal. The most
common aliasing is dithering on the fast edge.
The following two measures can avoid aliasing:
1. Increase the sampling frequency to more than twice the highest signal frequency;
2. Introduce or increase the parameters of the low-pass filter; the low-pass filter is often
called an anti-aliasing filter. Anti-aliasing filters can limit the bandwidth of the signal to
meet the conditions of the sampling theorem. In theory, this is feasible, but it is impos-
sible in practice. Because filters cannot completely filter out signals above the Nyquist
frequency, there is always some "small" energy outside the bandwidth required by the
sampling theorem. However, anti-aliasing filters can make these energies small enough
to be negligible.
Waveform distortion
Due to the low sampling rate, some waveform details are missing, which makes the
waveform displayed by the oscilloscope to be different from the actual waveform.
Waveform miss
Because the sampling rate is too low, the waveform when reconstructing the sampled
data does not reflect all the actual signals.