mathematical calculation used to remove outlying tails of a hyperbola and to accurately fix
the position of a target.
unit of measurement for recording the time delay between transmission of a radar pulse
and reception of that pulse’s reflections. Equal to one one-billionth of a second.
unwanted background interference that can obscure true data.
time depth at which the noise makes target identification impossible.
see Nano-Second.
device used to view and measure the strength and shape of energy waves. Common term
in GPR industry for a method of data display showing actual radar wave anatomy.
the frequency range at which the antenna is emitting energy. It is roughly equivalent to 0.5-2
times the center frequency.
Acronym for random access memory. Temporary memory in which a computer stores information
used with a running program, or temporarily stored data before it is written to a hard drive.
the total length of time (in nanoseconds) for which the control unit will record reflections. Note:
indicates two-way travel time.
Acronym for radio frequency.
a radar data point with two attributes: time and reflection amplitude. A third attribute, position,
is assigned by the user. Under-sampling will produce a scan wave that does not contain enough
information to draw a smooth curve. It may miss features. Over-sampling will produce a larger data file.
the number of samples recorded from an individual radar scan. Commonly set to 512.
one complete reflected wave from transmission to reception, sometimes called a trace.
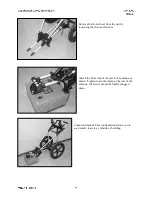
wheel attached to an antenna and calibrated to record precise distances. Necessary for
accurate data collection.
a horizontal planview of amplitude values drawn from adjacent vertical profiles. The time-
slice is produced for a particular time-depth and is vital for understanding the horizontal positions of
features in a survey area.
the amount of time, in nano-seconds, that the control unit will count reflections from a
particular pulse. Set by the operator.
a line of survey data. An area is systematically surveyed by recording transects of data at a
constant interval. The transects are then placed in their correct position relative to each other in a
computer and horizontal time-slices are produced.
Acronym for Ultra-Wide Band. Refers to the wide frequency band of emissions put out by a GPR
device.
method of GPR data display showing oscilloscope trace scans placed next to each other to
form a profile view. Commonly used method in seismic studies.