321023
97
13.9 Restrictions
13.9.1 Symptoms
Restrictions in sealed system most often occur at capillary tube or filter drier, but can exist anywhere
on liquid side of system.
Restrictions reduce refrigerant flow rate and heat removal rate. Wattage drops because compressor
is not circulating normal amount of refrigerants.
Common causes of total restrictions are moisture, poorly soldered joints, or solid contaminants.
Moisture freezes at evaporator inlet end of capillary tube. Solid contaminants collect in filter drier.
If restriction is on low side, suction pressure will be in a vacuum and head pressure will be near
normal.
If restriction is on high side, suction pressure will be in a vacuum and head pressure will be
higher than normal during pump out cycle.
Refrigeration occurs on low-pressure side of partial restriction. There will be a temperature
difference at the point of restriction. Frost and/or condensation will be present in most case at the
point of restriction. Also, system requires longer to equalize.
Slight or partial restriction can give the same symptoms as refrigerant shortage, including lower than
normal backpressure, head pressure, wattage, and warmer temperatures.
Total restriction on the discharge side of compressor, when restriction is between compressor and
first half of condenser, results in higher than normal head pressure and wattage while low side is
being pumped out.
13.9.2
Testing for Restrictions
To determine if a restriction exists:
1. Attach gauge and manifold between suction and discharge sides of sealed system.
2. Turn unit on and allow pressure on each side to stabilize. Inspect condenser side of system.
Tubing on condenser should be warm and temperature should be equal throughout (no sudden
drops at any point along tubing).
•
If temperature of condenser tubing is consistent throughout, go to step 4.
•
If temperature of condenser tubing drops suddenly at any point, tubing is restricted at point of
temperature drop (if restriction is severe, frost may form at point of restriction and extend down
in direction of refrigerant flow in system). Go to step 5.
3. Visually check system for kinks in refrigeration line which is causing restriction. Correct kink and
repeat step 2.
4. Turn unit off and time how long it takes high and low pressure gauges to equalize.
•
If pressure equalization takes longer than 10 minutes, a restriction exists in the capillary tube or
drier filter. Go to step 5.
•
If pressure equalization takes less than 10 minutes, system is not restricted. Check for other
possible causes of malfunction.
5. Recover refrigerant in sealed system.
NOTE:
Before opening any refrigeration system, capture refrigerant in system for safe disposal.
6. Remove power from unit.
CAUTION
To avoid risk of personal injury or property damage, take necessary precautions against high
temperatures required for brazing.
Summary of Contents for RX256DT4X1
Page 11: ...321023 11 2 3 Refrigerant Flow...
Page 12: ...321023 12 2 4 Cabinet Air Flow...
Page 13: ...321023 13 2 5 Ice And Water Dispenser Diagram...
Page 14: ...321023 14 2 6 Water Valve Diagram...
Page 15: ...321023 15 2 7 Typical External Sweat Pattern...
Page 16: ...321023 16 3 INSTALLATION...
Page 17: ...321023 17...
Page 18: ...321023 18...
Page 76: ...321023 76 Ice Water Dispensing Board...
Page 78: ...321023 78 Mid Electronic Specification Control RX256DT4X1 RX256ET2B1 RX256ET2W1...
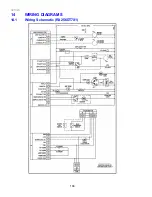
Page 104: ...321023 104 14 WIRING DIAGRAMS 14 1 Wiring Schematic RX256DT7X1...
Page 105: ...321023 105 14 2 Wiring Diagram RX256DT7X1...
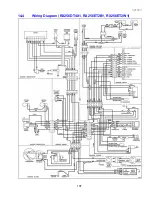
Page 106: ...321023 106 14 3 Wiring Schematic RX256DT4X1 RX256ET2B1 RX256ET2W1...
Page 107: ...321023 107 14 4 Wiring Diagram RX256DT4X1 RX256ET2B1 RX256ET2W1...
Page 108: ...321023 108 NOTES...