CHAPTER 13 S1C88 FAMILY DEBUGGER
S5U1C88000C MANUAL II
EPSON
109
WORKBENCH/DEV TOOLS/OLD ASSEMBLER
13.7.3 Executing from a Command File
Another method for executing commands is to use a command file that contains descriptions of a series
of debug commands. By reading a command file into the debugger the commands written in it can be
executed.
Creating a command file
Create a command file as a text file using an editor.
Although there are no specific restrictions on the extension of a file name, Seiko Epson recommends
using ".cmd".
Command files can also be created using the rec command. The rec command creates a command file
and saves the executed commands to the file.
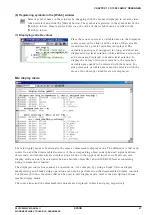
Example of a command file
The example below shows a command group that loads a program file, sets a breakpoint and then
executes the program.
Example: File name = start.cmd
lf test.abs
bp 0004d7
g
A command file to write the commands that come with a guidance mode can be executed. In this case,
be sure to break the line for each guidance input item as a command is written.
Reading in and executing a command file
The debugger has the com and cmw commands available that can be used to execute a command file.
The com command reads in a specified file and executes the commands in that file sequentially in the
order they are written.
The cmw command performs the same function as the com command except that each command is
executed at intervals specified by the md command (1 to 256 seconds).
Example:
com start.cmd
cmw test.cmd
The commands written in the command file are displayed in the [Command] window.
Restrictions
Another command file can be read from within a command file. However, nesting of these command
files is limited to a maximum of five levels. An error is assumed and the subsequent execution is
halted when the com or cmw command at the sixth level is encountered.