SIC63616-(Rev. 1.0) NO. P154
3240-0412
Since the reference resistance is oscillated until the measurement counter overflows, an appropriate
initial value needs to be set before R/f conversion is started. If a smaller initial value is set, a longer
counting period is possible, thereby ensuring more accurate detection. Convert the initial value into a
complement (value subtracted from "00000H") before setting it on the measurement counter. Since the
data output from the measurement counter after R/f conversion matches data detected by the sensor,
process the difference between that value and the initial value before it is converted into a complement
according to the program and calculate the target value.
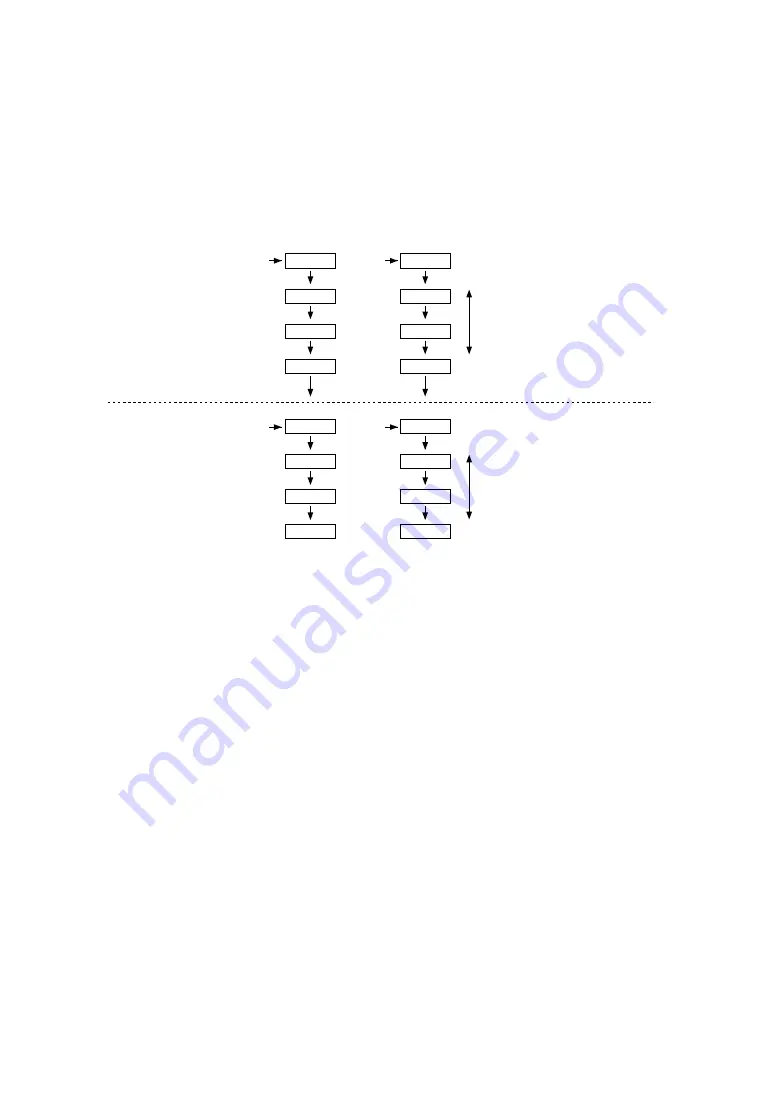
The above operations are shown in Figure 4.13.4.3.
Measurement counter
(MC)
(00000H-n)
(1) Set the initial value
00000H-n
00000H
Count up
FFFFFH
0
0
Count up
:
m
Time base counter
(TC)
00000H
Count down
:
x
x
FFFFFH
00000H
(2) Start reference oscillation
(Set RFRUNR to "1")
(3) Read the measurement counter and process the m - n value by the program
Setting by software
Set the complement of the initial
value n on the measurement counter.
Set "00000H" on the time base counter.
(Set "00000H" on the measurement counter.
Set x on the time base counter.)
Oscillation by
reference resistance
The CR oscillation stops when
the measurement counter overflows
and an interrupt occurs. Save the TC value
into the memory.
When the value of the time base
counter reaches "00000H",
oscillation and counting stop,
and an interrupt occurs.
Oscillation by
sensor
Count up
Reference oscillation
(1) Set the initial value
(00000H)
(x)
(2) Start sensor oscillation
(Set RFRUNS to "1")
Sensor oscillation
Fig. 4.13.4.3 Sequence of R/f conversion
Note: Set the initial value of the measurement counter taking into account the measurable range and the
overflow of counters.
4.13.5 Interrupt function
The R/f converter has a function which allows interrupt to occur when an R/f conversion has completed or
an error has occurred.
When the measurement counter reaches "00000H" during counting of the reference oscillation, both counters
stop counting and RFRUNR is set to "0". At the same time, the interrupt factor flag IRFR is set to "1".
When the time base counter reaches "00000H" during counting of the sensor oscillation, both counters stop
counting and RFRUNS is set to "0". At the same time, the interrupt factor flag IRFS is set to "1".
If the measurement counter overflows during counting of the sensor oscillation, both counters stop
counting and RFRUNS is set to "0". In this case, the interrupt factor flag IRFE is set to "1". At the same time,
the OVMC flag is also set to 1.
If the time base counter overflows during counting of the reference oscillation, both counters stop counting
and RFRUNR is set to "0". In this case, the interrupt factor flag IRFE is set to "1". At the same time, the
OVTC flag is also set to 1.
These interrupt factors allow masking by the interrupt mask registers EIRFR, EIRFS and EIRFE, and an
interrupt is generated to the CPU when these registers are set to "1". When the mask register is set to "0", an
interrupt is not generated to the CPU even if the interrupt factor flag is set to "1". The interrupt factor flag is
reset to "0" by writing "1".
Timing of interrupt by the R/f converter is shown in Figures 4.13.5.1 to 4.13.5.4.















































