75
Typ EP 501
Start-Up
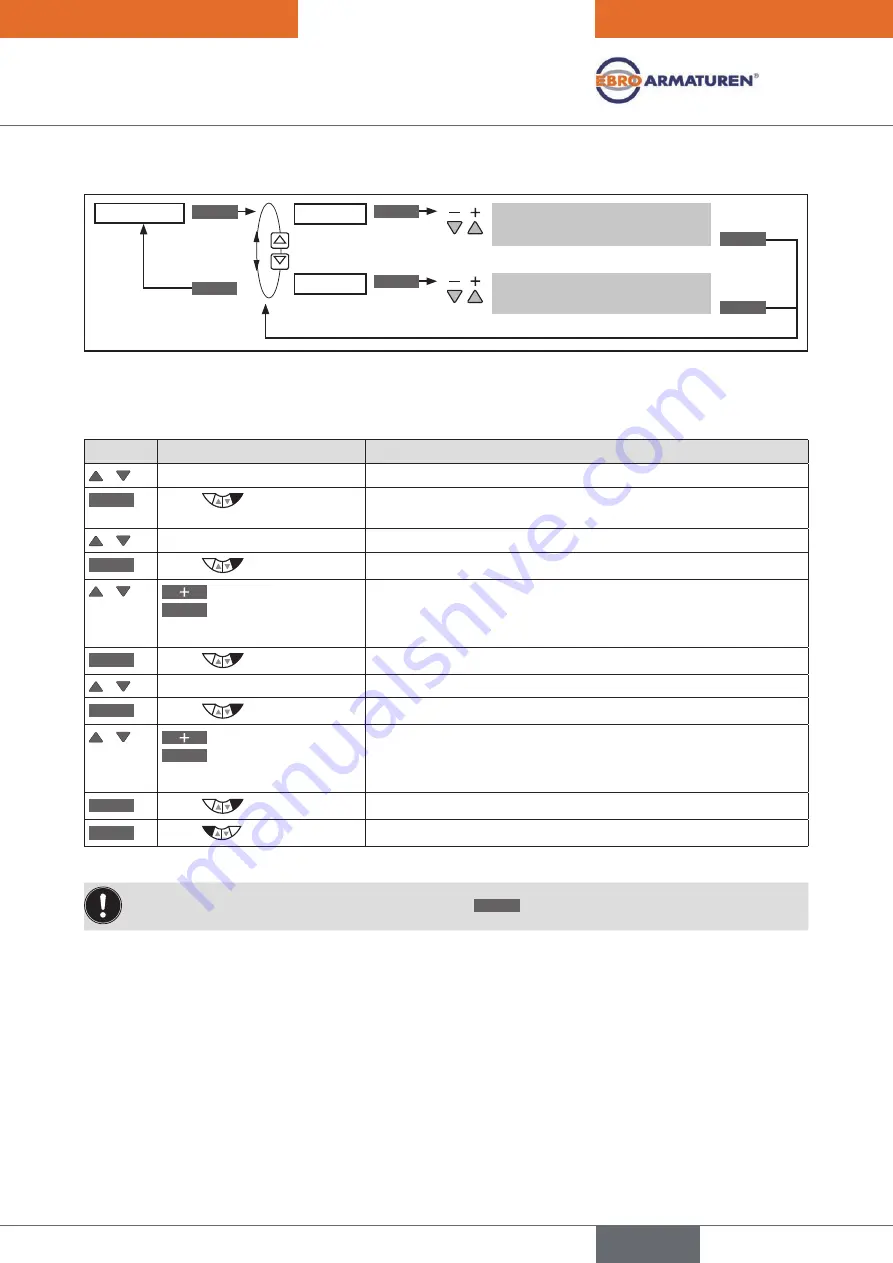
Operating structure:
*
ENTER
INPUT
INPUT
OK
OK
EXIT
SP-SCALE
SPmin
SPmax
Input upper process set-point
value
Input lower process set-point
value
*
Figure 31:
Operating structure SP-SCALE
Scaling.process.set-point.value.
SETUP
.
→
.
SP-SCALE
:
Key
Action
Description
/
Select
SP-SCALE
ENTER
Press
The submenu options for scaling of the process set-point value are
displayed.
/
Select
SPmin
INPUT
Press
The input screen is opened.
/
Increase value
<–
Select decimal place
Set scaling value (lower process set-point value).
The value is assigned to the smallest current or voltage value of the
standard signal.
OK
Press
Return to
SP-SCALE.
/
Select
SPmax
INPUT
Press
The input screen is opened.
/
Increase value
<–
Select decimal place
Set scaling value (upper process set-point value).
The value is assigned to the largest current or voltage value of the
standard signal.
OK
Press
Return to
SP-SCALE.
EXIT
Press
Return to
SETUP.
Table 34:
SP-SCALE; scaling process set-point value
If the submenu is left by pressing the left selection key
ESC
, the value remains unchanged.
english
















































