5-17
Catalyst 6000 Family Software Configuration Guide—Releases 6.3 and 6.4
78-13315-02
Chapter 5 Configuring Ethernet VLAN Trunks
Example VLAN Trunk Configurations
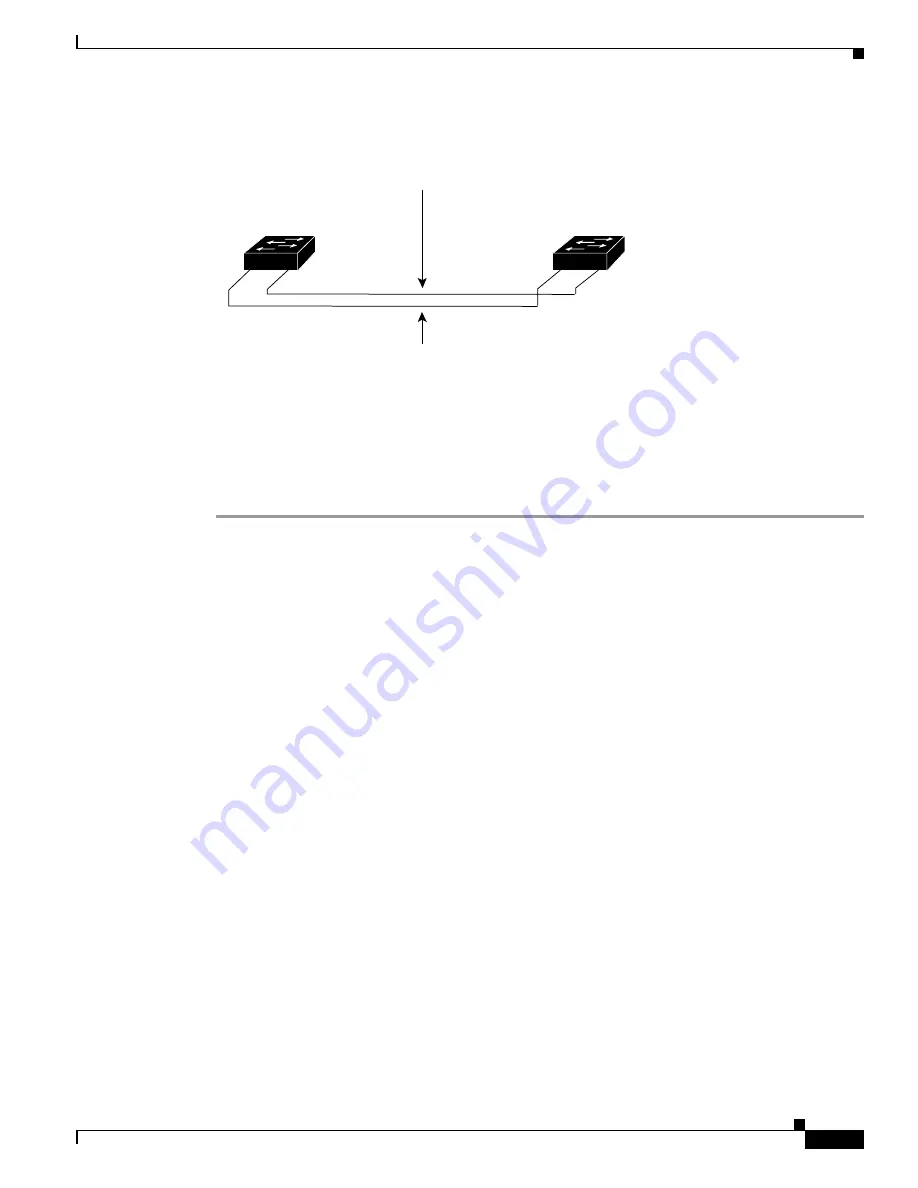
Figure 5-3
Parallel Trunk Configuration Before Configuring VLAN-Traffic Load Sharing
By default, the port-VLAN priority for both trunks is equal (a value of 32). STP blocks port 1/2
(Trunk 2) for each VLAN on Switch 1 to prevent forwarding loops. Trunk 2 is not used to forward traffic
unless Trunk 1 fails.
This example shows how to configure the switches so that traffic from multiple VLANs is load balanced
over the parallel trunks.
Step 1
Configure a VTP domain on both Switch 1 and Switch 2 by entering the
set vtp
command so that the
VLAN information configured on Switch 1 is learned by Switch 2. Make sure Switch 1 is a VTP server.
You can configure Switch 2 as a VTP client or as a VTP server.
Switch_1> (enable)
set vtp domain BigCorp mode server
VTP domain BigCorp modified
Switch_1> (enable)
Switch_2> (enable)
set vtp domain BigCorp mode server
VTP domain BigCorp modified
Switch_2> (enable)
Step 2
Create the VLANs on Switch 1 by entering the
set vlan
command. In this example, you see VLANs 10,
20, 30, 40, 50, and 60.
Switch_1> (enable)
set vlan 10
Vlan 10 configuration successful
Switch_1> (enable)
set vlan 20
Vlan 20 configuration successful
Switch_1> (enable)
set vlan 30
Vlan 30 configuration successful
Switch_1> (enable)
set vlan 40
Vlan 40 configuration successful
Switch_1> (enable)
set vlan 50
Vlan 50 configuration successful
Switch_1> (enable)
set vlan 60
Vlan 60 configuration successful
Switch_1> (enable)
Step 3
Verify the VTP and VLAN configuration on Switch 1 by entering the
show vtp domain
and
show vlan
commands.
Switch 1
Switch 2
Trunk 1
VLANs 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60: port-VLAN priority 32 (forwarding)
Trunk 2
VLANs 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60: port-VLAN priority 32 (blocking)
16750
1/1
1/2
1/1
1/2






























