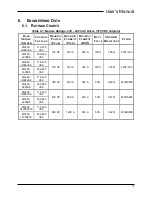
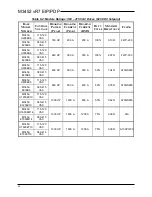
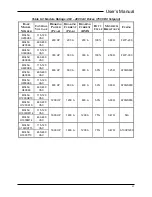
M3452 vR7 EIP/PDP
46
is any device on any network. On TCP/IP networks, each
host has one or more unique IP addresses. This module
connected to an Ethernet network may be referred to as a
host. An IP Address is a unique identification number for any
host (this module) on any TCP/IP network (including the
internet). The IP address is made up of four octets (8 bits),
each octet having a value between 0-255 (00h-FFh). The IP
address is comprised of two parts: the network address (first
part) and the host address (last part). The number of octets
of the four total that belong to the network address depend on
the Class definition (see below).
A
Static IP Address
is as the name implies
—static. That is, it
is a unique IP Address that is assigned by a service provider
and never changes.
A
Dynamic IP Address
is an address that is temporarily
assigned to a user by a service provider each time a user
connects.
A
Subnet
is a contiguous string of IP addresses. The first IP
address in a subnet is used to identify the subnet, while the
last IP address in a subnet is always used as a broadcast
address. Anything sent to the last IP address of a subnet is
sent to every host on that subnet.
Subnets are further broken down into three size classes
based on the 4 octets that make up the IP address. A Class
A subnet is any subnet that shares the first octet of the IP
address. The remaining 3 octets of a Class A subnet will
define up to 16,777,214 possible IP addresses (2
24
– 2). A
Class B subnet shares the first two octets of an IP address
(providing 2
16
– 2, or 65534 possible IP addresses). Class C
subnets share the first 3 octets of an IP address, giving 254
possible IP addresses. Recall that the first and last IP
addresses are always used as a network number and
broadcast address respectively, and this is why we subtract 2
from the total possible unique addresses that are defined via
the remaining octet(s).
For our example, the default IP address of this module is
128.1.1.100. If we assume that this is a Class C network
address (based on the default Class C subnet mask of
255.255.255.0), then the first three numbers represent this
Class C network at address 128.1.1.0, the last number
identifies a unique host/node on this network (node 100) at
address 128.1.1.100.
A
Subnet Mask
is used to determine which subnet an IP
address belongs to. The use of a subnet mask allows the
network administrator to further divide the host part of this
address into two or more subnets. The subnet mask flags the
network address portion of the IP address, plus the bits of the
host part that are used for identifying the sub-network. By
convention, the bits of the mask that correspond to the sub-
network address are all set to 1’s (it would also work if the bits
were set exactly as in the network address).
It’s called a
Summary of Contents for M3452
Page 14: ...M3452 vR7 EIP PDP 14 This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 19: ...User s Manual 19 Figure 3 2 Customer Connections in K9 Chassis CUSTOMER I 0 CONNECTION ...
Page 21: ...User s Manual 21 Figure 3 2 Customer Connections in M14 Chassis CUSTOMER I O CONNECTION ...
Page 24: ...M3452 vR7 EIP PDP 24 Figure 3 6 I O Hookup with R7 EIP PDP Communication ...
Page 26: ...M3452 vR7 EIP PDP 26 Figure 3 8 24VDC Power Connection ...
Page 58: ...M3452 vR7 EIP PDP 58 This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 66: ...M3452 vR7 EIP PDP 66 Figure 6 3 M3452 K9 Chassis Dimensional Outline Drawing ...
Page 68: ...M3452 vR7 EIP PDP 68 Figure 6 5 M3452 M14 Chassis Dimensional Outline Drawing ...
Page 75: ...User s Manual 75 NOTES ...
Page 76: ...M3452 vR7 EIP PDP 76 This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 77: ......
Page 78: ......
Page 79: ......