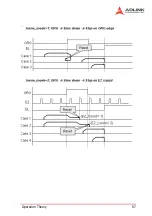
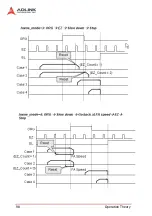
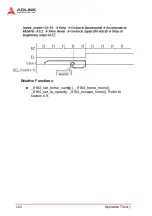
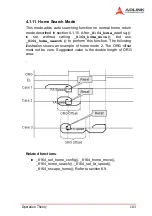
Operation Theory
107
4.2 The motor driver interface
The card provides the INP, ALM, ERC, SVON, and RDY signals
for a servomotor driver control interface. The INP and ALM are
used for feedback of the servo driver status, ERC is used to reset
the servo driver’s deviation counter under special conditions, VON
is a general purpose output signal, and RDY is a general purpose
input signal. General purpose means that the processing of the
signal is not a hardware built-in procedure. The hardware pro-
cesses INP, ALM, and ERC signals according to pre-defined rules.
For example, when receiving ALM signal, the card stops or decel-
erate to stop output pulses automatically. However, SVON and
RDY act like common I/Os.
4.2.1 INP
The processing of the INP signal is a hardware build-in procedure,
and it is designed to cooperate with the in-position signal of the
servomotor driver.
Usually, servomotor drivers with a pulse train input has a deviation
(position error) counter to detect the deviations between the input
pulse command and feedback counter. The driver controls the
motion of the servomotor to minimize the deviation until it
becomes 0. Theoretically, the servomotor operates with some time
delay from the command pulses. Likewise, when the pulse gener-
ator stops outputting pulses, the servomotor does not stop imme-
diately but keeps running until the deviation counter is zero. Only
after stopping does the servo driver send out the in-position signal
(INP) to the pulse generator to indicate the motor has stopped run-
ning.
If you do not enable INP checking by
_8164_set_inp()
func-
tion, the motion completion from
_8164_motion_done()
func-
tion and INT signal are raised after all pulses are sent.
If you enable INP checking by
_8164_set_inp()
function, the
motion completion from
_8164_motion_done()
function and
INT signal will not be raised until the INP signal from servo driver
is raised.
The in-position function can be enabled or disabled, and the input
logic polarity is also programmable by the “inp_logic” parameter of
Summary of Contents for MPC-8164
Page 4: ......
Page 12: ......
Page 14: ...2 Introduction Figure 1 1 PCI 8164 block diagram ...
Page 50: ...38 Installation ...
Page 70: ...58 Signal Connections ...
Page 74: ...62 Signal Connections 3 17 1 Isolated input channels 3 17 2 Isolated output channels ...
Page 75: ...Signal Connections 63 3 17 3 Example of input connection ...
Page 76: ...64 Signal Connections 3 17 4 Example of output connections ...
Page 109: ...Operation Theory 97 ...
Page 110: ...98 Operation Theory ...
Page 111: ...Operation Theory 99 ...
Page 112: ...100 Operation Theory ...
Page 113: ...Operation Theory 101 ...
Page 148: ...136 Operation Theory Users can use this function to check if auto trigger is running Results ...
Page 280: ...268 Connection Example Figure 7 2 Connection of PCI 8164 with Panasonic Driver ...
Page 287: ...Connection Example 275 7 3 3 Mechanical Dimensions ...
Page 297: ...Connection Example 285 7 5 2 Mechanical Dimensions ...
Page 300: ...288 Connection Example 7 6 Wiring with DIN 814M J3A ...
Page 304: ...292 Connection Example 7 7 Wiring with DIN 814Y ...
Page 308: ...296 ...