Chapter 9 •
Sensor Data
This chapter provides detailed information about sensor data characteristics.
9.1 Sensor Origin and Frame of Reference
9.2 Calculating X,Y,Z Coordinates from Collected Spherical Data
9.3 Packet Types and Definitions
9.3.3 Position Packet Structure
9.4 Discreet Point Timing Calculation
9.5 Precision Azimuth Calculation
9.6 Converting PCAP Files to Point Cloud Formats
9.1 Sensor Origin and Frame of Reference
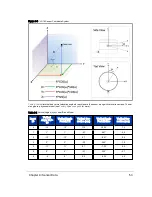
The sensor reports distances relative to itself in spherical coordinates (radius r, elevation ω, azimuth α). Sensor data origin
(0,0,0) is 37.7 mm above the sensor base, on the center axis, as shown in
(see the side and
top views), which also shows the sensor’s frame of reference. See also the mechanical/optical drawings in
Puck LITE Mechanical Drawing on page 102
9.2 Calculating X,Y,Z Coordinates from Collected Spherical Data
A computation is necessary to convert the spherical data (radius r, elevation ω, azimuth α) from the sensor to Cartesian
coordinates.
lists the formulas for converting spherical coordinates (R, ω, α) to Cartesian
coordinates (X, Y, Z).
52
VLP-16 User Manual
Содержание VLP-16
Страница 1: ...VLP 16 User Manual 63 9243 Rev D ...
Страница 64: ...Figure 9 9 Single Return Mode Timing Offsets in µs 64 VLP 16 User Manual ...
Страница 86: ...http 192 168 1 201 cgi setting laser on 204 OK Sensor laser is On motor rpm is 301 86 VLP 16 User Manual ...
Страница 106: ...C 6 Puck Hi Res Optical Drawing Figure C 6 Puck Hi Res OpticalDrawing 86 0129 Rev A 106 VLP 16 User Manual ...
Страница 109: ...D 1 Interface Box Wiring Diagram Figure D 1 Interface Box Wiring Diagram 86 0107A Appendix D Wiring Diagrams 109 ...
Страница 110: ...D 2 Interface Box Schematic Figure D 2 Interface Box Schematic 69 8230A 110 VLP 16 User Manual ...