O P E R AT I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | Bulkscan®
8014829/ZV98/2018-05-07| S I C K
Subject to change without notice
2 7
CONFIGURABLE FUNCTIONS
Behavior as pulse output
If the set
Volume quota
or Mass quota is reached, a pulse is transmitted from the digi-
tal output. You can set the
Pulse width
to between 20 ms and 10 s.
• Ensure that the set pulse width is as short as possible and as long as necessary for
the device connected to the digital output to still detect the pulse.
• Ensure that the duration of the pause between pulses is longer than the cycle time
resulting from the scan frequency (see "8.5 Scan frequency“ on page 72).
Behavior as switching output
The digital output is activated when the measured value falls below the set lower limit
value or exceeds the set upper limit. The output remains active until the measured
value lies within the set limit values again.
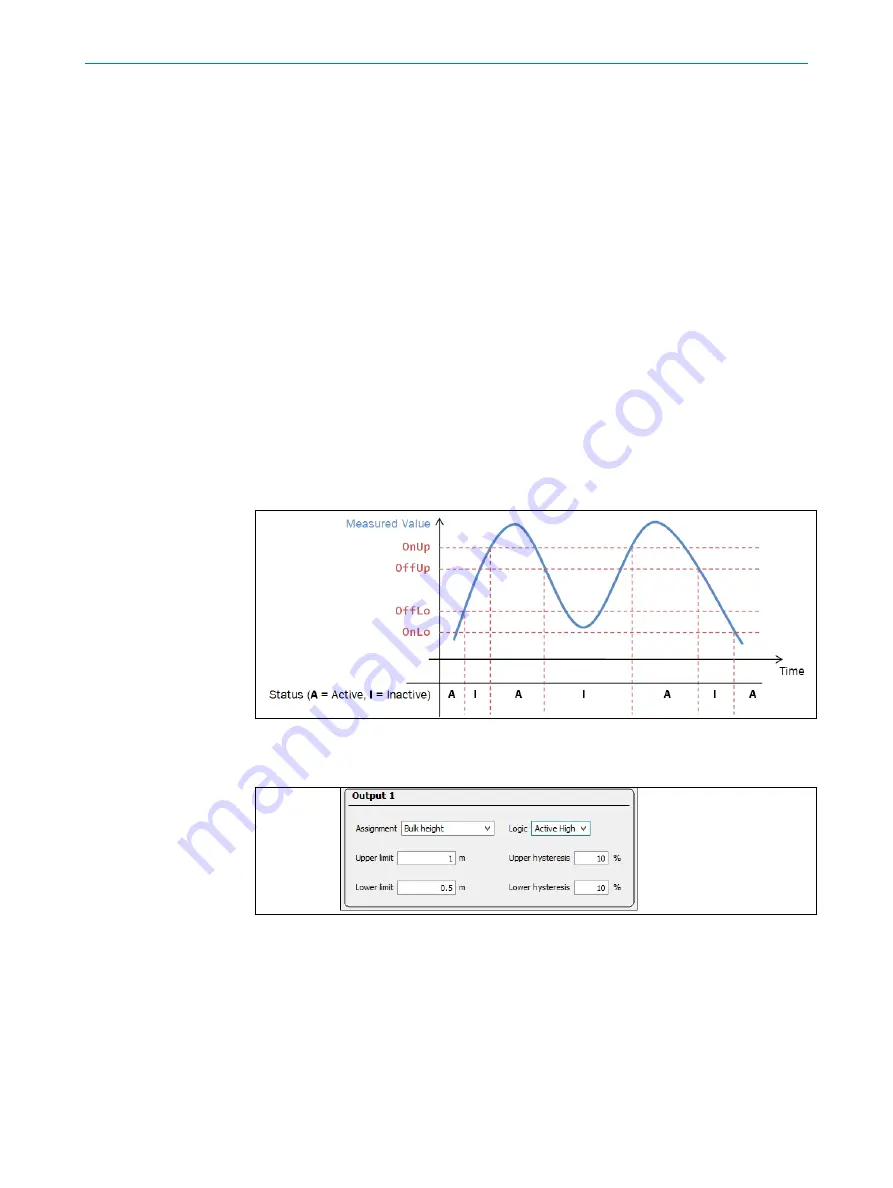
If the measured values fluctuate about the upper or lower limit value, the digital output
would switch continuously. In practice, this behavior is not desirable. This is prevented
by the configurable Hysteresis.
From the upper and lower limits and their respective hysteresis, upper and lower switch-
ing limits are calculated as follows:
Switch on limit high: OnUp= (1 + (
Upper hysteresis
/ 100)) ×
Upper limit
Switch off limit high: OffUp = (1 - (
Upper hysteresis
/ 100)) ×
Upper limit
Switch off limit low: OffLo = (1 + (
Lower hysteresis
/ 100)) ×
Lower limit
Switch on limit low: OnLo = (1 - (
Lower hysteresis
/ 100)) ×
Lower limit
Fig. 10: Switching limits representations with relevant hysteresis
Example: The digital Output1 is selected as Bulk height with following settings.
Fig. 11: digital Output1 set as Bulk height rate and settings
Under these conditions the switching limits are defined as follow:
OnUp = (1 + (
Upper hysteresis
/ 100)) ×
Upper limit
= (1+10/100) x 1 = 1.1 m
OffUp = (1 - (
Upper hysteresis
/ 100)) ×
Upper limit
= (1-10/100) x 1 = 0.9 m
OffLo = (1 + (
Lower hysteresis
/ 100)) ×
Lower limit
= (1+10/100) x 0,5 = 0.55 m
OnLo = (1 - (
Lower hysteresis
/ 100)) ×
Lower limit
= (1-10/100) x 0,5 = 0.45 m
• A small hysteresis increases the switching frequency at the limit value.
• A large hysteresis reduces the switching frequency at the limit value.
Note
Note
















































