7–Installing Management Applications
Detailed Procedures
82
83840-546-00 D
Set up Namespace Security Using WMI Control
The WMI Control provides one way to manage namespace security. You can start
the WMI Control from the command prompt using this command:
wmimgmt
On Windows 9x or Windows NT4 computers that have WMI installed, use this
command instead:
wbemcntl.exe
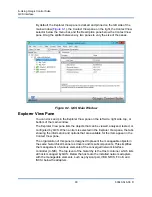
Alternatively, you can access the WMI Control and the Security tab as follows:
1.
Right-click on
My Computer
and click
Manage
.
2.
Double-click
Services and Applications
and then double-click
WMI
Control
.
3.
Right-click
WMI Control
and then click
Properties
.
4.
In WMI Control Properties, click the
Security
tab.
5.
A folder named Root with a plus sign (+) next to it should now be visible.
Expand this tree as necessary to locate the namespace for which to set
permissions.
6.
Click
Security
.
A list of users and their permissions appears. If the user is on the list, modify
the permissions as appropriate. If the user is not on the list, click
Add
and
add the user from the location (local machine, domain) where the account
resides.
NOTE
You can add these exports at the end of the
.bash_profile
file. This file is
located in the
/root
directory.
To view and set namespace security, the user must have Read Security
and Edit Security permissions. Administrators have these permissions
by default, and can assign the permissions to other user accounts as
required.
If this user needs to access the namespace remotely, you must select
the Remote Enable permission.
By default, user permissions set on a namespace apply only to that
namespace. If you want the user to have access to a namespace and all
subnamespaces in the tree below it, or in subnamespaces only, click
Advanced
. Click
Edit
and specify the scope of access in the dialog box.