EI65 Operator’s and Calibration Handbook
L-B B5L0082/PAT 031-300-190-015 REVISION D 04/15/99
3 ESSENTIAL INFORMATION AND SETUP FOR CALIBRATION:
3.1 Prior to powering up the system verify all wiring. All unused channels must be occupied
with dummy signals meeting the following requirements.
•
The second angle channel must have a voltage divider installed. Install two 4.7k resistors,
one between X1 #21-22 and the other between X1 #22-23.
•
The second and third A2B channels must have a 4.7k resistor. Install a 4.7k resistor
between X1 #11-12 and X1 #13-14.
•
The second force channel must have a jumper installed between X1 #30-31.
•
A no load system must have a jumper installed between X1- #26-27, for the first force
channel.
3.1 Mechanically set the length and angle sensors as follows: (See Appendix A. Mechanical
Adjustment for Sensors).
•
Length Sensor - With the boom sections fully retracted set the length potentiometer by
turning the center screw counter clockwise slowly to a soft stop.
•
Angle Sensors: Align the angle sensors with the boom at zero degrees.
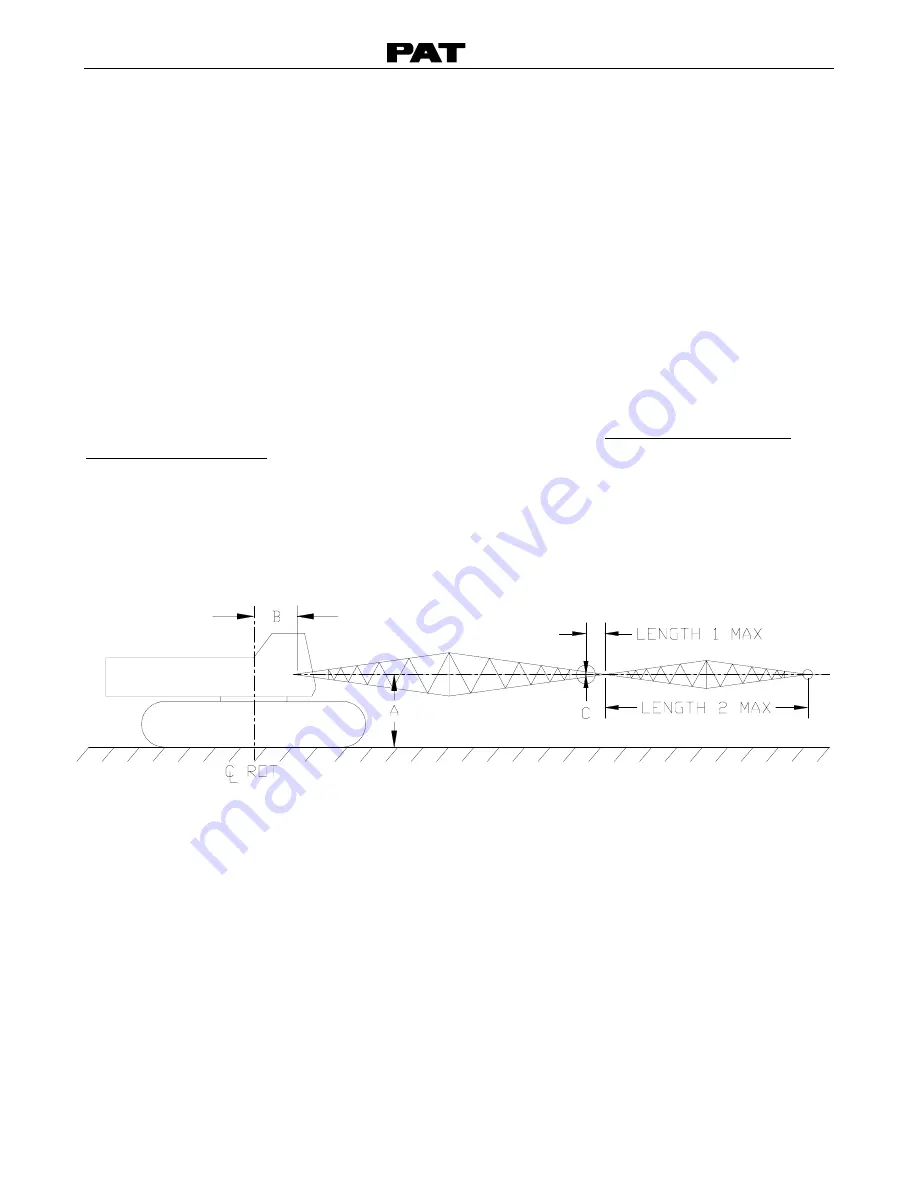
Write down the following geometric measurements, which will be used during calibration. (See
Figure 1. Crane Measurements). The measurements taken should be in units that correspond
to the load chart.(i.e. lbs/feet, Kg/meters, US-Tons/feet, Metric-ton/meters).
Figure 1. Crane Measurements
A. The vertical distance from the boom foot pivot pin to the ground. The calibration
procedure refers to this dimension as “High Offset.” (see Section 4.6.2)
B. The horizontal distance from the boom foot pivot pin to the center line of rotation. The
calibration procedure refers to this dimension as “Rad Offset.” (see Section 4.6.3)
C. The head offset, which is the vertical measurement between the boom foot pivot pin to
the lower head sheave center pin. The calibration procedure refers to this dimension as
“Head Offset.” (see Section 4.6.4)
D. Jib extension lengths minimum and maximum














































