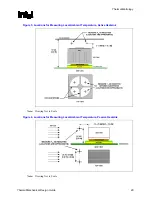
Thermal Management Logic and Thermal Monitor Feature
R
Thermal/Mechanical Design Guide
31
4
Thermal Management Logic and
Thermal Monitor Feature
4.1
Processor Power Dissipation
An increase in processor operating frequency not only increases system performance, but also
increases the processor power dissipation. The relationship between frequency and power is
generalized in the following equation: P = CV
2
F (where P = power, C = capacitance,
V = voltage, F = frequency). From this equation, it is evident that power increases linearly with
frequency and with the square of voltage. In the absence of power saving technologies, ever
increasing frequencies will result in processors with power dissipations in the hundreds of watts.
Fortunately, there are numerous ways to reduce the power consumption of a processor, and Intel
is aggressively pursuing low power design techniques. For example, decreasing the operating
voltage, reducing unnecessary transistor activity, and using more power efficient circuits can
significantly reduce processor power consumption.
An on-die thermal management feature called Thermal Monitor is available on the Pentium 4
processor in the 775–land LGA package. It provides a thermal management approach to support
the continued increases in processor frequency and performance. By using a highly accurate on-
die temperature sensing circuit and a fast acting Thermal Control Circuit (TCC), the processor can
rapidly initiate thermal management control. The Thermal Monitor can reduce cooling solution
cost, by allowing thermal designs to target TDP.
4.2
Thermal Monitor Implementation
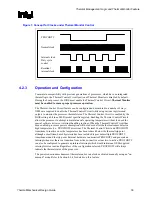
On the Pentium 4 processor in the 775–land LGA package, the Thermal Monitor is integrated into
the processor silicon includes:
•
A bi-directional signal (PROCHOT#) that indicates if the processor has exceeded its
maximum temperature or can be asserted externally to activate the Thermal Control Circuit
(TCC).
•
A Thermal Control Circuit that will attempt to reduce processor temperature by rapidly
reducing power consumption when the on-die temperature sensor indicates that it has
exceeded the maximum operating point.
•
Registers to determine the processor thermal status.
Содержание 640 - Pentium 4 640 3.2GHz 800MHz 2MB Socket 775 CPU
Страница 14: ...Introduction R 14 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide ...
Страница 38: ...Thermal Management Logic and Thermal Monitor Feature R 38 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide ...
Страница 52: ...Intel Thermal Mechanical Reference Design Information R 52 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide ...
Страница 60: ...Acoustic Fan Speed Control R 60 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide ...
Страница 72: ...Heatsink Clip Load Metrology R 72 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide ...
Страница 97: ...Mechanical Drawings R Thermal Mechanical Design Guide 97 Figure 48 Reference Clip Drawings Sheet 1 ...
Страница 98: ...Mechanical Drawings R 98 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide Figure 49 Reference Clip Drawings Sheet 2 ...
Страница 99: ...Mechanical Drawings R Thermal Mechanical Design Guide 99 Figure 50 Reference Fastener Sheet 1 ...
Страница 100: ...Mechanical Drawings R 100 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide Figure 51 Reference Fastener Sheet 2 ...
Страница 101: ...Mechanical Drawings R Thermal Mechanical Design Guide 101 Figure 52 Reference Fastener Sheet 3 ...
Страница 102: ...Mechanical Drawings R 102 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide Figure 53 Reference Fastener Sheet 4 ...
Страница 103: ...Mechanical Drawings R Thermal Mechanical Design Guide 103 Figure 54 Clip Heatsink Assembly ...
Страница 104: ...Mechanical Drawings R 104 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide Figure 55 Intel R RCBFH 3 Reference Solution Assembly ...