Thermal Metrology
R
28
Thermal/Mechanical Design Guide
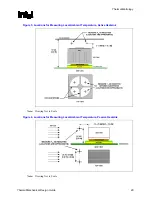
should be placed approximately 3 mm to 8 mm [0.1 to 0.3 in] above the fan hub vertically and
halfway between the fan hub and the fan housing horizontally as shown in Figure 5 (avoiding the
hub spokes). Using an open bench to characterize an active heatsink can be useful, and usually
ensures more uniform temperatures at the fan inlet. However, additional tests that include a solid
barrier above the test motherboard surface can help evaluate the potential impact of the chassis.
This barrier is typically clear Plexiglas*, extending at least 100 mm [4 in] in all directions beyond
the edge of the thermal solution. Typical distance from the motherboard to the barrier is 81 mm
[3.2 in]. For even more realistic airflow, the motherboard should be populated with significant
elements like memory cards, graphic card, and chipset heatsink. If a barrier is used, the
thermocouple can be taped directly to the barrier with a clear tape at the horizontal location as
previously described, half way between the fan hub and the fan housing. If a variable speed fan is
used, it may be useful to add a thermocouple taped to the barrier above the location of the
temperature sensor used by the fan to check its speed setting against air temperature. When
measuring T
A
in a chassis with a live motherboard, add-in cards, and other system components, it
is likely that the T
A
measurements will reveal a highly non-uniform temperature distribution
across the inlet fan section.
For
passive
heatsinks
, thermocouples should be placed approximately 13 mm to 25 mm
[0.5 to 1.0 in] away from processor and heatsink as shown in Figure 6. The thermocouples should
be placed approximately 51 mm [2.0 in] above the baseboard. This placement guideline is meant
to minimize the effect of localized hot spots from baseboard components.
Note:
Testing an active heatsink with a variable speed fan can be done in a thermal chamber to capture
the worst-case thermal environment scenarios. Otherwise, when doing a bench top test at room
temperature, the fan regulation prevents the heatsink from operating at its maximum capability.
To characterize the heatsink capability in the worst-case environment in these conditions, it is
then necessary to disable the fan regulation and power the fan directly, based on guidance from
the fan supplier.
Содержание 640 - Pentium 4 640 3.2GHz 800MHz 2MB Socket 775 CPU
Страница 14: ...Introduction R 14 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide ...
Страница 38: ...Thermal Management Logic and Thermal Monitor Feature R 38 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide ...
Страница 52: ...Intel Thermal Mechanical Reference Design Information R 52 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide ...
Страница 60: ...Acoustic Fan Speed Control R 60 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide ...
Страница 72: ...Heatsink Clip Load Metrology R 72 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide ...
Страница 97: ...Mechanical Drawings R Thermal Mechanical Design Guide 97 Figure 48 Reference Clip Drawings Sheet 1 ...
Страница 98: ...Mechanical Drawings R 98 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide Figure 49 Reference Clip Drawings Sheet 2 ...
Страница 99: ...Mechanical Drawings R Thermal Mechanical Design Guide 99 Figure 50 Reference Fastener Sheet 1 ...
Страница 100: ...Mechanical Drawings R 100 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide Figure 51 Reference Fastener Sheet 2 ...
Страница 101: ...Mechanical Drawings R Thermal Mechanical Design Guide 101 Figure 52 Reference Fastener Sheet 3 ...
Страница 102: ...Mechanical Drawings R 102 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide Figure 53 Reference Fastener Sheet 4 ...
Страница 103: ...Mechanical Drawings R Thermal Mechanical Design Guide 103 Figure 54 Clip Heatsink Assembly ...
Страница 104: ...Mechanical Drawings R 104 Thermal Mechanical Design Guide Figure 55 Intel R RCBFH 3 Reference Solution Assembly ...