54
Network Guide
TP/FT 10 Network Topologies
The physical routing of the communication channel defines the network topology. The channel
and transceiver types define the requirements and limitations of each wiring topology.
TP/FT 10 network segments require termination for proper data transmission performance.
Free topology and bus network topology differ in their termination requirements. The following
sections describe the various network topologies, their terminator types and termination pro-
cedures.
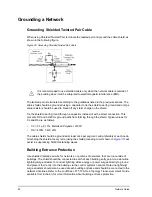
Bus Topology
A bus topology is a physical routing of the communication channel that includes a distinct
beginning and end. It is also known as a daisy-chain topology.
Figure 32: Figure 3 3: Bus Topology
TP/FT 10 Bus Topology Network Termination
For bus topology type networks, use the following terminators at each end of the bus topology
channel (2 terminators per channel in total):
R1 = 105Ω, ±1%, ⅛W
C1 = 100µF, ≥50V
C2 = 100µF, ≥50V
It is recommended to use a bus topology when designing a network. Bus topologies
are the easiest to troubleshoot and the maximum wiring length in a bus topology is
greater than that for a free topology. See
on page 55 for detailed
information about wiring lengths and network cable considerations.
Содержание ECB-VAV
Страница 1: ...User Guide Network Guide...
Страница 6: ...Table of Contents 4 Network Guide...
Страница 52: ...50 Network Guide...
Страница 70: ...68 Network Guide...
Страница 110: ...108 Network Guide...
Страница 121: ...LonWorks Troubleshooting Network Guide 119...
Страница 122: ...120 Network Guide...
Страница 124: ...122 Network Guide...
Страница 128: ...126 Network Guide...
Страница 134: ...132 Network Guide Figure 75 Example of How to Set a DIP Switch to 82 ON B A For example 82 A 1010 B 010...
Страница 136: ...134 Network Guide...
Страница 137: ...Network Guide...
Страница 138: ...Network Guide_UG_24_EN...