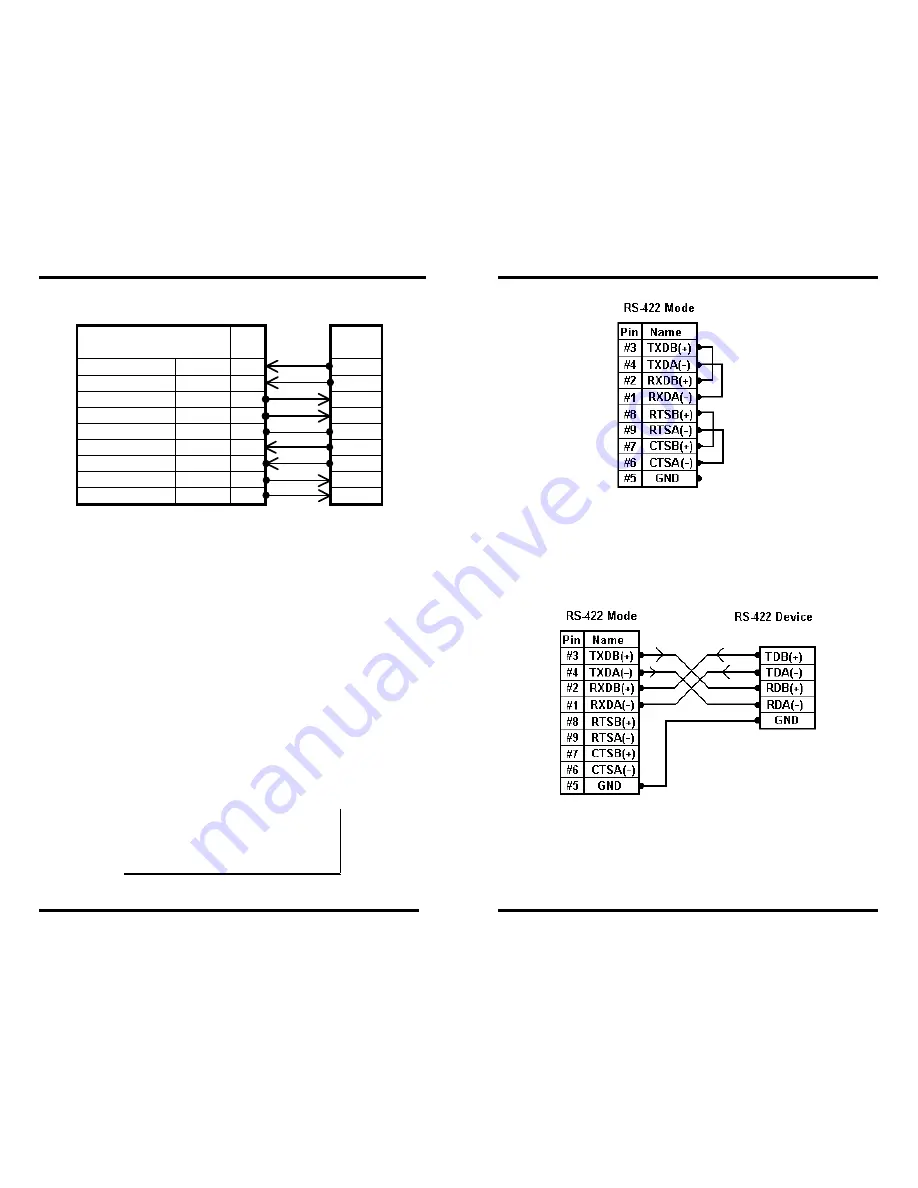
RS-422
Connections
75
Figure 68. RS-422 Connections with Flow Control
In the RS-422 mode, TXD lines are outputs and RXD lines are inputs.
Connect the
XTRALINK IP
TXDB(+) line to the RXDB(+) line of the
serial device, and the
XTRALINK IP
TXDA(-) to the RXDA(-) of the
serial device.
If Flow Control is set for RTS/CTS
, connect the
XTRALINK IP
RTSB(+) to CTSB(+) of the serial device and the
XTRALINK IP
RTSA(-) line to the CTSA(-) of the serial device. Connect from the
XTRALINK IP
CTSB(+) line to the RTSB(+) of the serial device and
from the
XTRALINK IP
CTSA(-) line to the RTSB(+) line of the serial
device.
If connecting to Receive Only
RS-422 devices, connect from the
XTRALINK IP
TXDB(+) and TXDA(-) lines to the receive pairs on all
serial devices.
Ground is signal ground and provides a common mode reference for
the RS-422 Receiver and Transmitters.
N
N
o
o
t
t
e
e
:
:
The RS-422 mode can be used for full duplex 4-wire RS-485 operation
provided that the XTRALINK IP is acting as a sole master connecting
to all the slave devices, and all slave devices share the Receive signal
lines to the master. Set Flow Control for none, and omit connections to
RTS/CTS line pairs.
XTRALINK IP
pin-out
in RS-422 mode
RS-422
Device
RS-422 Signal Names
DB-9
Pin#
Connections
Signal
Receive A (-)
RXDA(-)
1
TDA(-)
Receive B (+)
RXDB(+)
2
TDB(+)
Transmit B (+)
TXDB(+)
3
RDB(+)
Transmit A (-)
TXDA(-)
4
RDA(-)
Ground
GND 5
GND
Clear to Send A (-)
CTSA(-)
6
RTSA(-)
Clear to Send B (+)
CTSB(+)
7
RTSB(+)
Ready to Send B (+) RTSB(+)
8
CTSB(+)
Ready to Send A (-) RTSA(-)
9
CTSA(-)
RS-422
Connections
76
Figure 69. Loopback Connections for RS-422
The RS-485 Connections are half duplex, either Receive or Transmit,
so another half duplex device must be used to check operation.
Figure 70. RS-422 Connection with No Flow Control




































