5.3.7
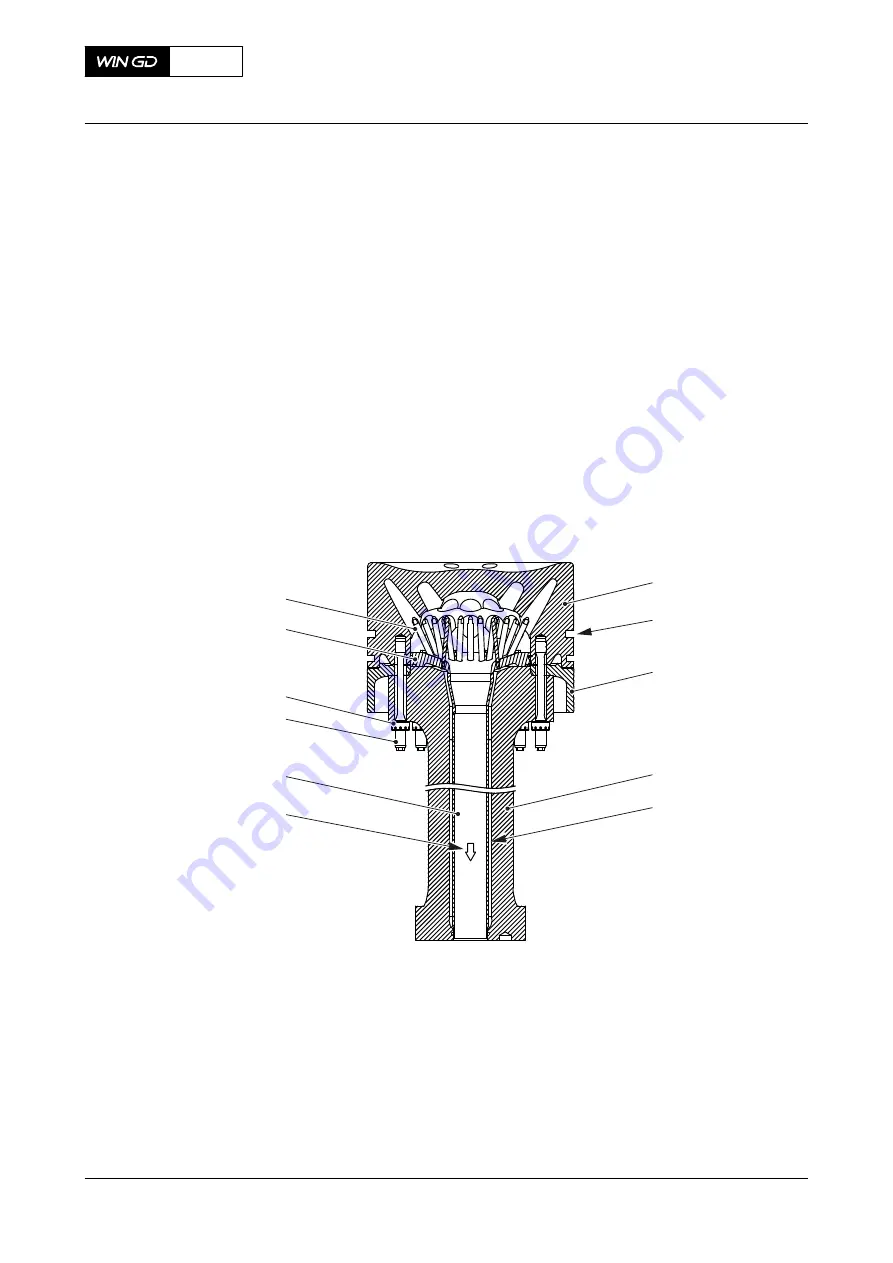
Piston
The piston moves in each cylinder. The piston rings seal the combustion chamber. The piston
transmits the force from the gas that expands in the cylinder to the crankshaft through the
connecting rod.
Elastic bolts (008,
) and round nuts (009) attach the piston crown (001) to the piston
rod (004). The piston skirt (003) is attached to the piston rod with screws. The piston rod (004) is
attached to the crosshead pin in a specified position. The compression shims are installed between
the piston rod and the crosshead pin. The thickness of the compression shims is related to the
specified compression ratio.
System oil is used to keep cool the piston crown (001). This oil flows from the crosshead pin into
the space (005) between the oil pipe (007) and the piston rod (004). The oil then flows to the spray
plate (010). The oil comes out as a spray from the nozzles (011) into the cooling bores of the piston
crown (001). The oil then flows through the oil pipe (007) into the crosshead pin and out through
the oil bores to the crankcase.
Fig 5-21
Piston (example)
003
002
001
004
011
008
007
006
009
010
005
Legend
001
Piston crown
007
Oil pipe (from piston crown)
002
Piston ring groove
008
Elastic bolt
003
Piston skirt
009
Round nut
004
Piston rod
010
Spray plate
005
Space
011
Nozzle
006
Oil flow
X52
AA00-3403-00AAA-043A-A
Operation Manual
Piston
Winterthur Gas & Diesel Ltd.
- 150 -
Issue 002 2018-11