VAMP Ltd
Feeder and motor manager
Technical description
VAMP 257
VM257.EN002
VAMP 24h support phone : +358 (0)20 753 3264
67
frequency back to the original value. However, in case of a
heavy short circuit fault or in case the new load exceeds the
generating capacity, the average frequency keeps on
decreasing.
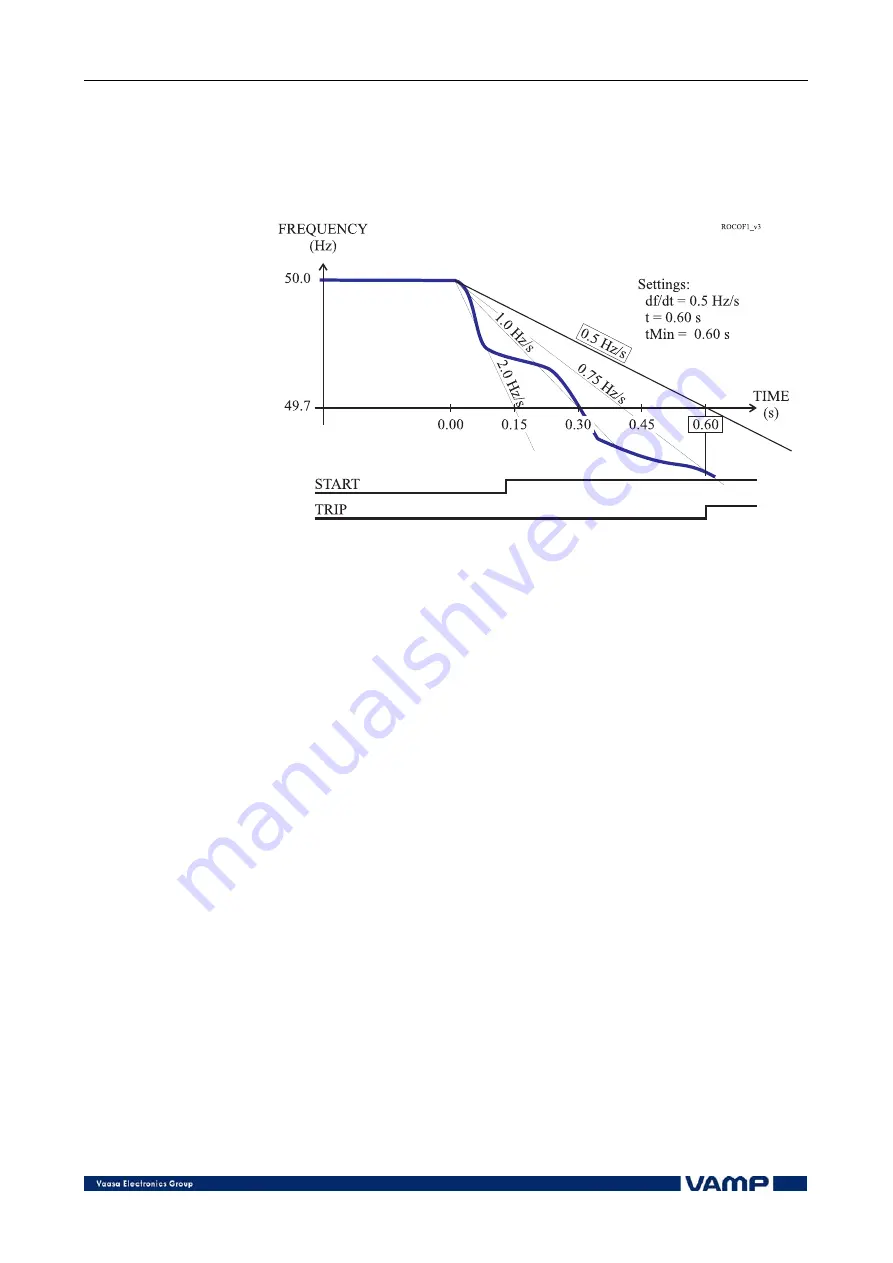
Figure 2.3.22-1 An example of definite time df/dt operation time. At 0.6 s,
which is the delay setting, the average slope exceeds the setting 0.5 Hz/s
and a trip signal is generated.
Description of ROCOF implementation
The ROCOF function is sensitive to the absolute average value
of the time derivate of the measured frequency |df/dt|.
Whenever the measured frequency slope |df/dt| exceeds the
setting value for 80 ms time, the ROCOF stage picks up and
issues a start signal after an additional 60 ms delay. If the
average |df/dt|, since the pick-up moment, still exceeds the
setting, when the operation delay time has elapsed, a trip
signal is issued. In this definite time mode the second delay
parameter "minimum delay, t
Min
" must be equal to the
operation delay parameter "t".
If the frequency is stable for about 80 ms and the time t has
already elapsed without a trip, the stage will release.
ROCOF and frequency over and under stages
One difference between over-/under-frequency and df/dt
function is the speed. In many cases a df/dt function can
predict an overfrequency or underfrequency situation and is
thus faster than a simple overfrequency or underfrequency
function. However, in most cases a standard overfrequency
and underfrequency stages must be used together with ROCOF
to ensure tripping also in case the frequency drift is slower
than the slope setting of ROCOF.






























