XIIMUS 4K CL User Manual. Model: 4096CT. Version 1.4
3. CAMERA
OVERVIEW
3.1 Colour
Separation
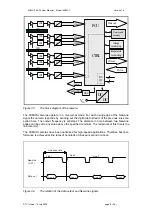
The incoming light is separated into three, Red,
Green and Blue, colour images by an RGB beam
splitter (figure 3.1). The spectral distribution of each
colour is standardised and well known. By attaching
a CCD to each of these colour outputs, it is possible
to measure the intensity of each colour image.
BLUE
GREEN
RED
INCOMING LIGHT
Figure 3.1
The RGB colour separation beam splitter.
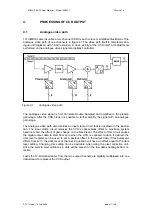
The CCDs are aligned to each other
to get the perfect image of the three
measured colour components. All
the three CCDs see exactly the
same area of the target from same
viewing angle, distance and at the
same time. Corresponding pixels of
all the three sensors are very
precisely positioned optically in the
same place. This makes the colour
analysis simpler and does not
require any line matching or
synchronising of separate colour
lines. The resolution of the camera
is the same as for the individual
CCD array.
R
G
B
RGB color line
3 x CCD
Figure 3.2. Alignment of the CCD linear arrays.
3.2 Camera
Operation
The CCDs convert incoming light into electrical charge. The amount of charge generated in
each of the individual pixels is directly proportional to the intensity of light they receive. The
resulting charge packets are transferred into two high-speed CCD shift registers and trans-
ferred to the output charge-to-voltage converters of the CCDs. The generated output video is
Correlate Double Sampled (CDS) and amplified by two user accessible gain factors prior to
digitisation into 12 bits.
© TVI Vision, 14 July 2006 page 8 ( 56 )