(GLWLRQ
6WDUWXS
Siemens AG 6SE8004-0BH76
SIMOVERT MV Commissioning Instructions
63
4.3.4
Checking the angular offset
In order to be able to check the angular offset, the closed-loop control must be
changed-over into setpoint generator operation (refer to Section 4.3.2). Refer to
Section 4.3.3 when enabling the analog outputs.
The following settings should be made in the FP-TRV:
♦
Connect KPW1.GW to S4.X1. Connect the oscilloscope, channel 1 at -A132
terminals X2:7 and X2:8.
♦
Connect KPW2.GW to S5.X1. Connect the oscilloscope, channel 2 to -A132
terminals X2:9 and X2:10.
Set the gain factors DA4.SF and DA5.SF to #3.15.
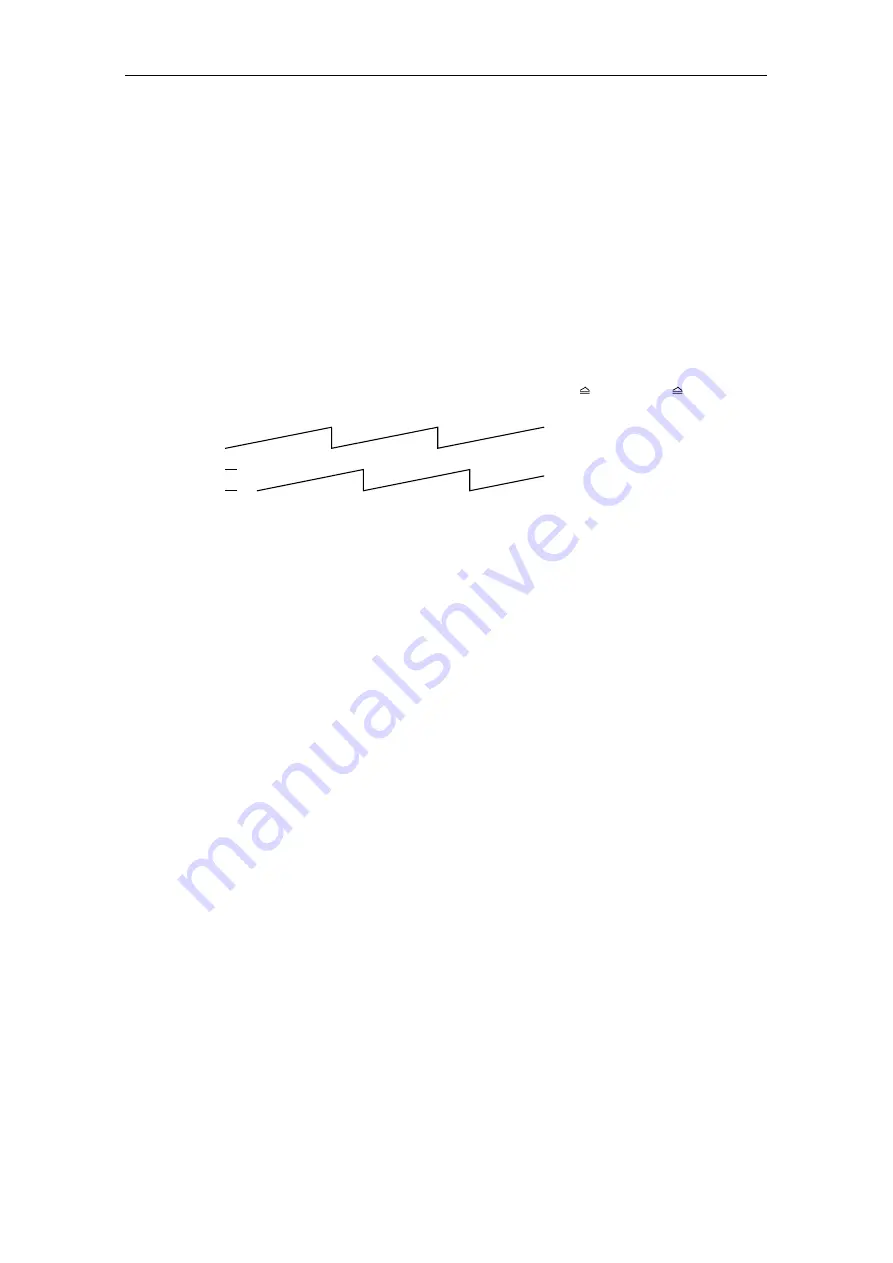
This then allows the angle of the voltage vector and the current vector to be
displayed on the oscilloscope as sawtooth signals (0 V 0 and 10 V value at
2
π
). The following is displayed for a clockwise rotating field:
0
2
π
10 V
Voltage angle
Current angle
At a constant speed, the sawtooth must increase with a constant gradient between
0 and 2
π
. Signal noise and disturbances (jumps upwards or downwards) indicate
that the signal sensing is faulty (hardware problem).
The voltage vector angle must lead the current vector angle by 90° when the motor
is in a no-load condition.
4.3.5
Checking the speed sensing (operation with encoder)
In order to check the speed sensing, the closed-loop control must be changed-over
into the setpoint encoder mode (refer to Section 4.3.2). Values can be output from
the FP-TRV. In this case, a frequency setpoint (e.g. 2 Hz) must be entered.
In order to check the speed sensing, the electrical and the mechanical angles must
be prepared. The values from FG.YP (mechanical angle 0
⇒
1 signifies clockwise
rotation, 0
⇒
−
1 signifies counter-clockwise rotation) and LWA.WLS (electrical
angle) should be output, normalized to
π
, at analog outputs (Output refer to Section
4.3.3 and Section 4.3.4) (the angle runs from 0
⇒
2
π
). These two angles must fulfill
the following condition: LWA.WLS = DP.PP * FG.YP, whereby DP.PP corresponds
to the pole pair number. In the following, the mechanical frequency must be
compared with the electrical frequency. This can be realized via the Telemaster.
The actual values can be read at the blocks FG.Y (f
mechanical
) and WFA.FLS (f
electrical
)
in function package TRV. The values which have been read should be
approximately numerically the same as those of the frequency setpoint.
Different frequency setpoints must be used when checking.
















































