STEP 5 Operations
S5-95F
8.1.3
Load and Transfer Operations
Use load and transfer operations to do the following tasks.
•
Exchange information between various operand areas
•
Prepare time and count values for further processing
•
Load constants for program processing
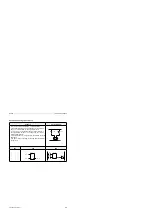
Information flows indirectly via accumulators (ACCU 1 and ACCU 2). The accumulators are special
registers in the programmable controller that serve as temporary storage. They are each 16 bits
long. The accumulators are structured as shown in Figure 8-1.
ACCU 2
ACCU 1
15
8
7
0
15
8
7
0
Low byte
High byte
Low byte
High byte
Figure 8-1. Accumulator Structure
You can load and transfer permissible operands in bytes or words. For exchange in bytes, infor-
mation is stored right-justified, i.e., in the low byte.
The remaining bits are set to zero.
You can use various operations to process the information in the two accumulators.
Load and transfer operations are executed independently of condition codes. Execution of these
operations does not affect the condition codes.
You can program load and transfer operations graphically only in combination with timer or counter
operations; otherwise you can represent them only in STL form.
Table 8-3 provides an overview of the load and transfer operations. Examples follow the table.
8-10
EWA 4NEB 812 6210-02