RUGGEDCOM ROS
User Guide
Chapter 5
Setup and Configuration
Managing Multicast Filtering
217
Section 5.8
Managing Multicast Filtering
Multicast traffic can be filtered using IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) snooping or GMRP (GARP
Multicast Registration Protocol).
CONTENTS
•
Section 5.8.1, “Managing IGMP”
•
Section 5.8.2, “Managing GMRP”
Section 5.8.1
Managing IGMP
IGMP is used by IP hosts to report their host group memberships with multicast routers. As hosts join and leave
specific multicast groups, streams of traffic are directed to or withheld from that host.
The IGMP protocol operates between multicast routers and IP hosts. When an unmanaged switch is placed
between multicast routers and their hosts, the multicast streams will be distributed to all ports.This may introduce
significant traffic onto ports that do not require it and receive no benefit from it.
IGMP Snooping, when enabled, will act on IGMP messages sent from the router and the host, restricting traffic
streams to the appropriate LAN segments.
IMPORTANT!
RUGGEDCOM ROS restricts IGMP hosts from subscribing to the following special multicast addresses:
• 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255
• 224.0.1.129
These addresses are reserved for routing protocols and IEEE 1588. If an IGMP membership report
contains one of these addresses, the report is forwarded by the switch without learning about the host.
CONTENTS
•
Section 5.8.1.1, “IGMP Concepts”
•
Section 5.8.1.2, “Viewing a List of Multicast Group Memberships”
•
Section 5.8.1.3, “Viewing Forwarding Information for Multicast Groups”
•
Section 5.8.1.4, “Configuring IGMP”
Section 5.8.1.1
IGMP Concepts
The following describes some of the concepts important to the implementation of multicast filtering using IGMP:
IGMP In Operation
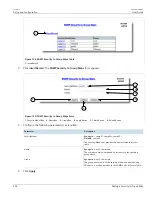
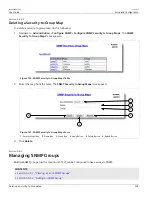
The following network diagram provides a simple example of the use of IGMP.