User's Guide Fireface 802
© RME
79
26. The Matrix
26.1 Overview
The mixer window of TotalMix looks and operates similar to mixing desks, as it is based on a
conventional stereo design. The matrix display presents a different method of assigning and
routing channels, based on a single channel or monaural design. The matrix view of the Fire-
face 802 has the look and works like a conventional patchbay, adding functionality way beyond
comparable hardware and software solutions. While most patchbays will allow you to connect
inputs to outputs with just the original level (1:1, or 0 dB, as known from mechanical patchbays),
TotalMix allows you to use a freely definable gain value per crosspoint.
Matrix and TotalMix are different ways of displaying the same processes. Because of this both
views are always fully synchronized. Each change in one view is immediately reflected in the
other view as well.
26.2 Elements of the Matrix View
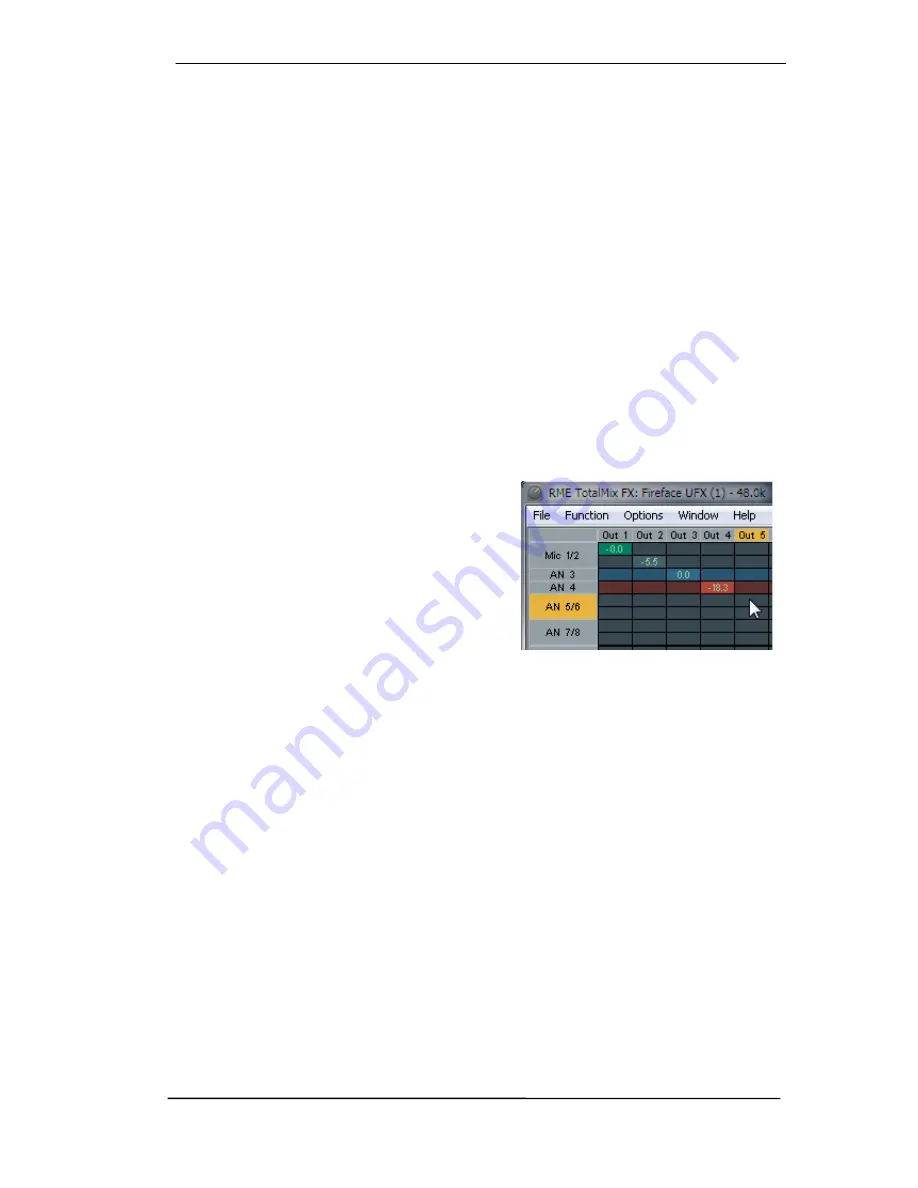
The visual design of the TotalMix Matrix is mainly determined by the architecture of the Fireface
802 system:
¾
Horizontal labels.
All hardware outputs
¾
Vertical labels.
All hardware inputs. Below are
all playback channels.
¾
Green 0.0 dB field.
Standard 1:1 routing
¾
Dark grey field with number.
Shows the
current gain value as dB
¾
Blue field.
This routing is muted
¾
Red field.
Phase 180° (inverted)
¾
Dark grey field.
No routing.
To maintain overview when the window size has been reduced, the labels are floating. They
won't leave the visible area when scrolling.
26.3 Operation
Using the Matrix is a breeze. It is very easy to indentify the current crosspoint, because the
outer labels light up in orange according to the mouse position.
¾
If input 1 is to be routed to output 1, use the mouse and click one time on crosspoint
In 1
/
AN 1
with held down Ctrl key. Two green 0.0 dB field pop in, another click removes them.
¾
To change the gain (equals the use of a different fader position, see simultaneous display of
the mixer view), drag the mouse up or down, starting from the gain field. The value within the
field changes accordingly. The corresponding fader in the mixer view is moving simultane-
ously, in case the currently modified routing is visible.
¾
On the right side is the Control Strip from the mixer window, adapted to the Matrix. The but-
ton for the temporary fader group is missing as well as all View options, as they don’t make
sense here. Instead the button
Mono Mode
lets you decide whether all the actions per-
formed in the Matrix are valid for two channels or just one.
Summary of Contents for Fireface 802
Page 7: ...User s Guide Fireface 802 RME 7 User s Guide Fireface 802 General...
Page 12: ...12 User s Guide Fireface 802 RME...
Page 13: ...User s Guide Fireface 802 RME 13 User s Guide Fireface 802 Installation and Operation Windows...
Page 28: ...28 User s Guide Fireface 802 RME...
Page 29: ...User s Guide Fireface 802 RME 29 User s Guide Fireface 802 Installation and Operation Mac OS X...
Page 38: ...38 User s Guide Fireface 802 RME...
Page 39: ...User s Guide Fireface 802 RME 39 User s Guide Fireface 802 Inputs and Outputs...
Page 47: ...User s Guide Fireface 802 RME 47 User s Guide Fireface 802 Stand Alone Operation...
Page 50: ...50 User s Guide Fireface 802 RME...
Page 51: ...User s Guide Fireface 802 RME 51 User s Guide Fireface 802 TotalMix FX...
Page 53: ...User s Guide Fireface 802 RME 53...
Page 89: ...User s Guide Fireface 802 RME 89 User s Guide Fireface 802 Class Compliant Mode...
Page 94: ...94 User s Guide Fireface 802 RME...
Page 95: ...User s Guide Fireface 802 RME 95 User s Guide Fireface 802 Technical Reference...
Page 106: ...106 User s Guide Fireface 802 RME 36 Diagrams 36 1 Block Diagram Fireface 802...
Page 108: ...108 User s Guide Fireface 802 RME...
Page 109: ...User s Guide Fireface 802 RME 109 User s Guide Fireface 802 Miscellaneous...






























