User Manual
E727T0005, valid for E-727
BRO, 2019-06-28
Physik Instrumente (PI) GmbH & Co. KG, Auf der Roemerstrasse 1, 76228 Karlsruhe, Germany
Page 114 / 240
Phone +49 721 4846-0, Fax +49 721 4846-1019, Email
Dynamic Digital Linearization (DDL)
Dynamic Digital Linearization (DDL) makes it possible to achieve significantly better position
accuracy in dynamic applications with periodic motion. It is used in conjunction with the wave
generator output and in addition to the servo algorithm in closed-loop operation of an axis. DDL
"observes" axis motion over one or more wave generator output cycles (DDL initialization). The
information gathered is written to "DDL tables" and can then be used to refine the control output
signals.
"Working Principle" (p. 114) describes the DDL basics, "How to Activate the DDL Licence" (p. 117)
gives information on how to get the DDL started the first time, in "How to work with the DDL"
(p. 118) you will learn how to use the DDL feature, and "DDL-Related Commands and Parameters"
(p. 198) gives a summary.
See also "Wave Generator" (p. 99).
Working Principle
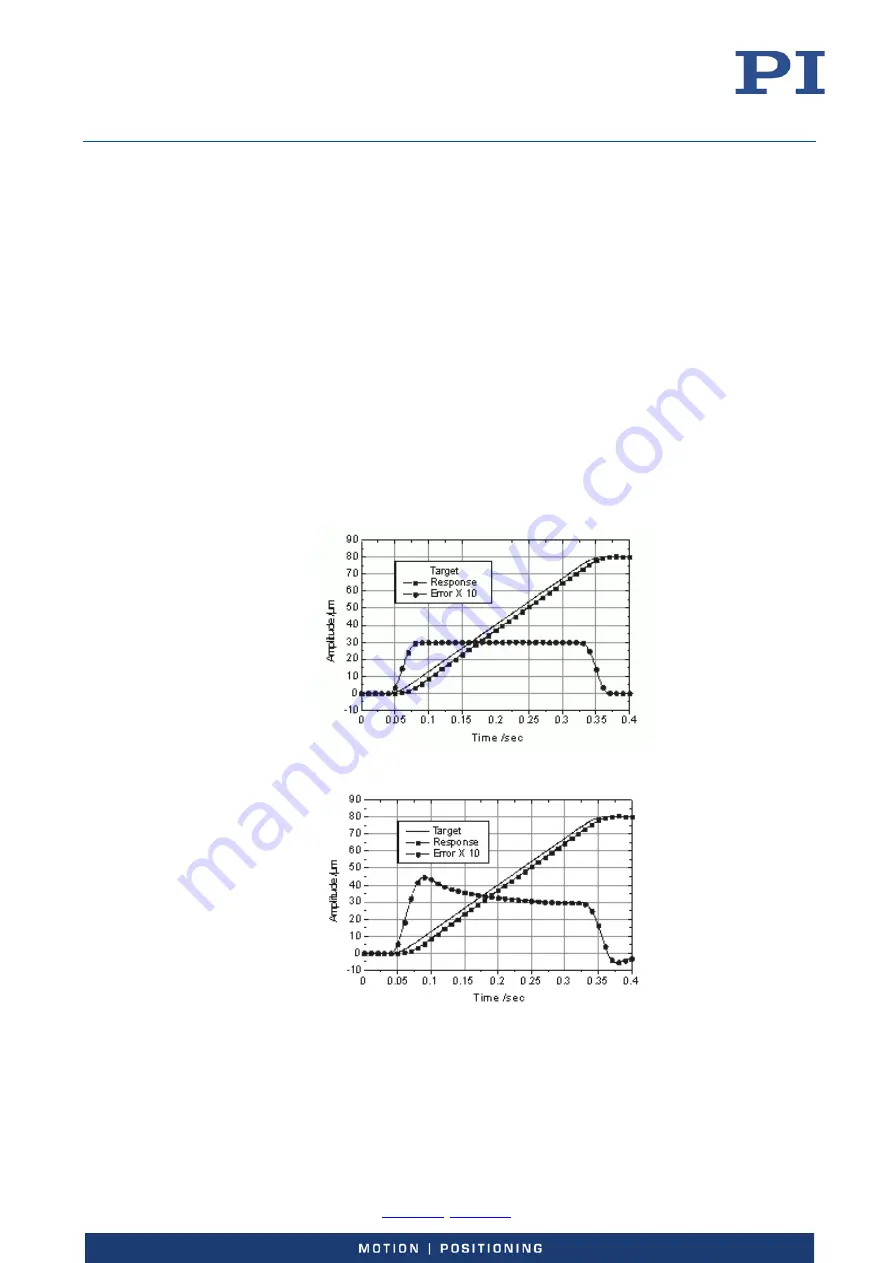
The tracking error of a standard piezo servo-controller is practically zero at very low speeds but
increases with the operating frequency of the axis.
Figure 31: Tracking error for typical linear PID servo system
Figure 32: Tracking error for linear bi-directional scanning application






























