•
Printing inks, paint removers, varnishes, etc.
•
Hydrochloric acid
•
Cements and glues
•
Antistatic fabric softeners for clothes dryers
•
Masonry acid washing materials
All fuel-burning equipment must be supplied with air for fuel combustion. Sufficient air must be provided to avoid negative pressure in the
equipment room or space. A positive seal must be made between the furnace cabinet and the return-air duct to prevent pulling air from the burner
area and from draft safeguard opening.
WARNING: CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING HAZARD
The operation of exhaust fans, kitchen ventilation fans, clothes dryers, attic exhaust fans or fireplaces could create a NEGATIVE
PRESSURE CONDITION at the furnace. Make-up air MUST be provided for the ventilation devices, in addition to that required by the
furnace. Refer to the Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Hazard warning in the venting section of these instructions to determine if an
adequate amount of make-up air is available.
The requirements for combustion and ventilation air depend upon whether or not the furnace is located in a space having a volume of at least 50
cubic feet per 1,000 Btuh input rating for all gas appliances installed in the space.
•
Spaces having less than 50 cubic feet per 1,000 Btuh require the OUTDOOR COMBUSTION AIR METHOD.
•
Spaces having at least 50 cubic feet per 1,000 Btuh may use the INDOOR COMBUSTION AIR, STANDARD or KNOWN-AIR
INFILTRATION METHOD.
Outdoor Combustion Air Method
1. Provide the space with sufficient air for proper combustion, ventilation, and dilution of flue gases using permanent horizontal or vertical
duct(s) or opening(s) directly communicating with the outdoors or spaces that freely communicate with the outdoors.
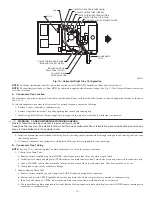
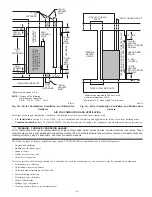
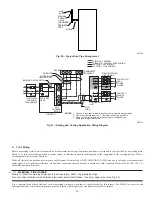
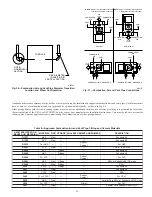
2. Fig. 18 illustrates how to provide TWO OUTDOOR OPENINGS, one inlet and one outlet combustion and ventilation air openings to the
outdoors.
a. One opening MUST commence within 12
″
(300 mm) of the ceiling and the second opening MUST commence within 12
″
(300 mm) of
the floor.
b. Size openings and ducts per Fig. 18 and Table 1.
c. TWO HORIZONTAL DUCTS require 1 square inch of free area per 2,000 Btuh (1,100 mm
2
/kW) of combined input for all gas
appliances in the space per Fig. 18 and Table 1.
d. TWO OPENINGS OR VERTICAL DUCTS require 1 square inch of free area per 4,000 Btuh (550 mm
2
/kW) for combined input of all
gas appliances in the space per Fig. 18 and Table 1.
3. ONE OUTDOOR OPENING requires:
a. 1 square inch of free area per 3,000 Btuh (734 mm
2
/kW) for combined input of all gas appliances in the space per Table 1 and
b. Not less than the sum of the areas of all vent connectors in the space.
The opening shall commence within 12
″
(300 mm) of the ceiling. Appliances in the space shall have clearances of at least 1
″
(25 mm)
from the sides and back and 6
″
(150 mm) from the front. The opening shall directly communicate with the outdoors or shall communicate
through a vertical or horizontal duct to the outdoors or spaces (crawl or attic) that freely communicate with the outdoors.
Indoor Combustion Air© NFPA & AGA
Standard and Known-Air-Infiltration Rate Methods
Indoor air is permitted for combustion, ventilation, and dilution, if the Standard or Known-Air-Infiltration Method is used.
WARNING: CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING HAZARD
Failure to supply outdoor air via grilles or ducts could result in death and/or personal injury.
Many homes require air to be supplied from outdoors for furnace combustion, ventilation, and dilution of flue gases.
The furnace combustion air supply must be provided in accordance with this instruction manual.
The Standard Method:
1. The space has no less volume than 50 cubic feet per 1,000 Btuh of the maximum input ratings for all gas appliances installed in the space
and
2. The air infiltration rate is not known to be less than 0.40 air changes per hour (ACH).
The Known Air Infiltration Rate Method shall be used, if the infiltration rate is known to be:
1. Less than 0.40 ACH and
2. Equal to or greater than 0.10 ACH
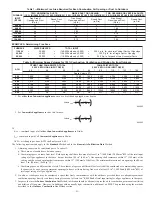
Infiltration rates greater than 0.60 ACH shall not be used. The minimum required volume of the space varies with the number of ACH and shall
be determined per Table 2 or Equations 1 and 2. Determine the minimum required volume for each appliance in the space and add the volumes
together to get the total minimum required volume for the space.
Table 3-Minimum Space Volumes were determined by using the following equations from the National Fuel Gas Code ANSI Z223.1-2002/NFPA
54-2002,8.3.2.2:
—20—
Summary of Contents for PG9MAA
Page 70: ... 70 ...
Page 71: ... 71 ...