124
|
Chapter 7. Advanced Settings (Part 1)
N300 Wireless Dual Band ADSL2+ Modem Router DGND3300v2 User Manual
•
Your primary Internet access is through a cable modem to an ISP.
•
You have an ISDN router on your home network for connecting to the company where
you are employed. This router’s address on your LAN is
1
92.168.0.100.
•
Your company’s network address is 134.177.0.0.
When you first configured your N300 wireless modem router, two implicit static routes were
created. A default route was created with your ISP as the gateway, and a second static route
was created to your local network for all 192.168.0.x addresses. With this configuration, if you
attempt to access a device on the 134.177.0.0 network, your N300 wireless modem router
forwards your request to the ISP. The ISP forwards your request to the company where you
are employed, and the request is likely to be denied by the company’s firewall.
In this case you must define a static route, telling your N300 wireless modem router that
134.177.0.0 should be accessed through the ISDN router at 192.168.0.100.
In this example:
•
The Destination IP Address and IP Subnet Mask fields specify that this static route applies
to all 134.177.x.x addresses.
•
The Gateway IP Address field specifies that all traffic for these addresses should be
forwarded to the ISDN router at 192.168.0.100.
•
A Metric value of 1 will work since the ISDN router is on the LAN.
•
Private is selected only as a precautionary security measure in case RIP is activated.
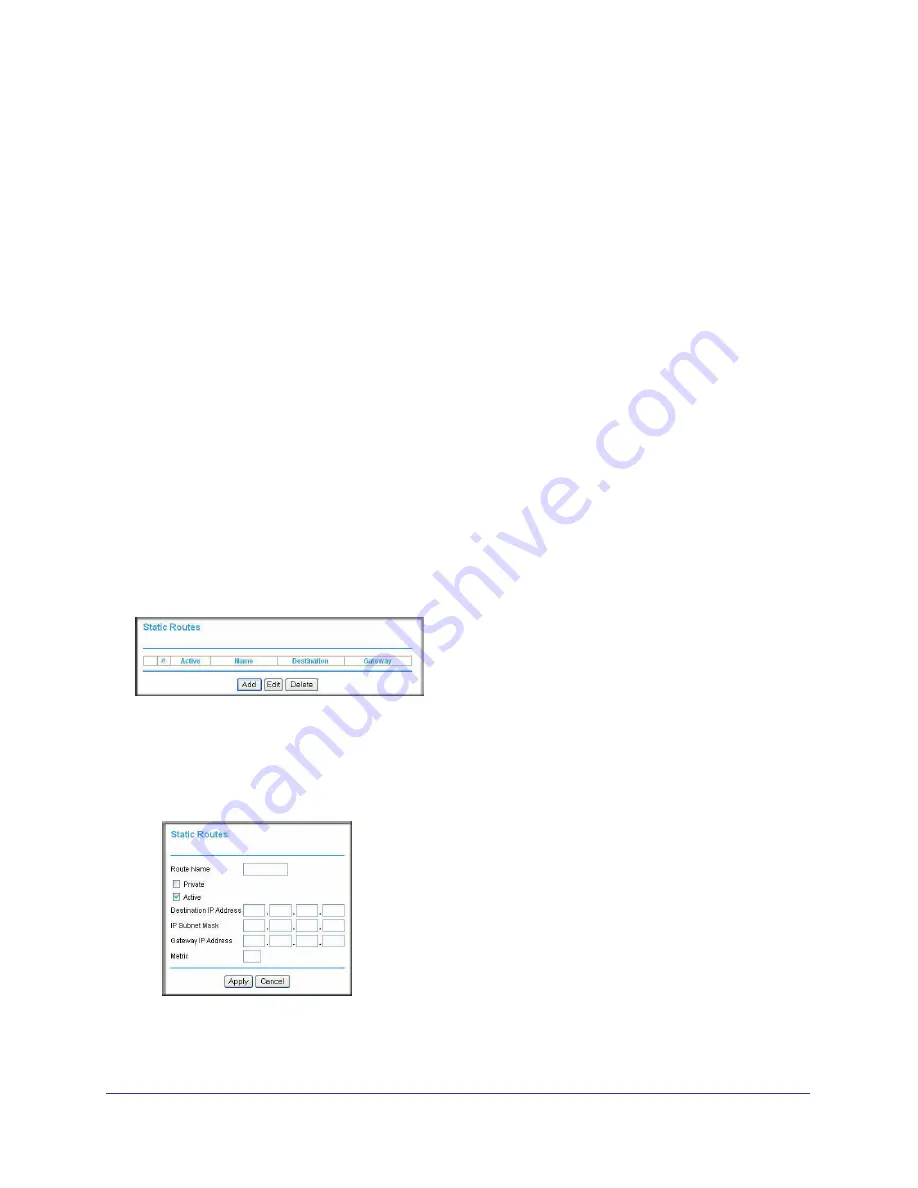
From the main menu, select
Advanced > Static Routes
. The Static Routes screen displays.
Figure 64.
To add or edit a static route:
1.
Click
Add
to open the Static Routes screen.
Figure 65.






























