8. AUXILIARY AND APPLIED FUNCTIONS
8
−
16
8.8 Teaching
Function
The teaching function allows the operator to teach the servo system CPU when the
target position (address) is unknown or to align with an object.
(1) Teaching methods
Two teaching methods are available: "address teaching" and "program
teaching."
(a) Address teaching
Writes the current value to the designated program address.
The program must be created before the address teaching method can be
used.
(b) Program teaching
Writes the current value to addresses while the program is being created.
(2) For details about teaching, see the A30TU-E Teaching Unit Operating Manual
(IB-67277).
8.9 High
−−−−
Speed Reading of Designated Data
This function stores the designated positioning data in the designated device
(
D,
W
)
with the signal from an input module mounted on the motion slot of the motion
base as the trigger.
It can be set in the system setting of a peripheral device software package.
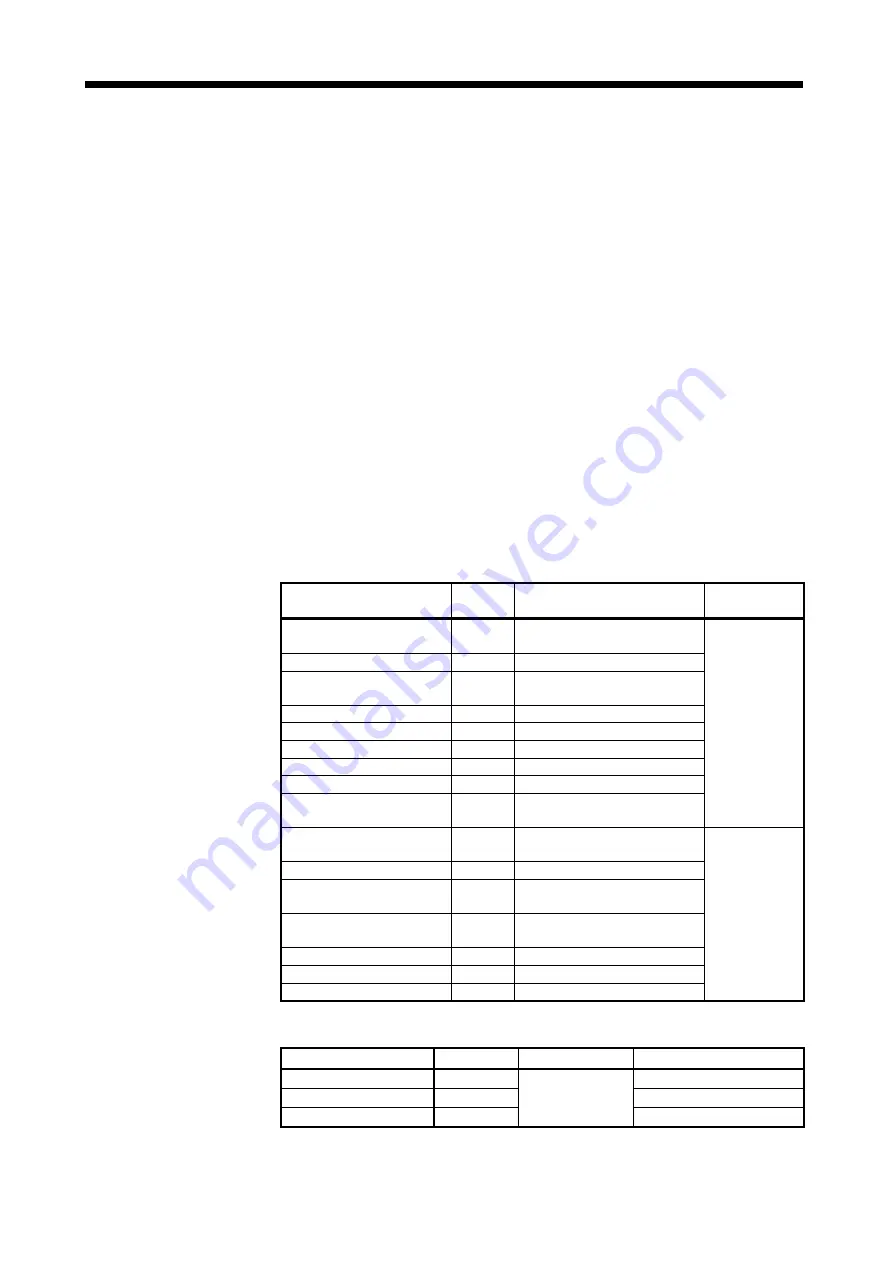
(1) Positioning data that can be set
Set Data
Number
of Words
Unit
Remarks
Position command
(feed current value)
2
10
-1
µ
m
•
10
-5
inch
•
10
-5
degree
•
PLS
Real current value
2
10
-1
µ
m
•
10
-5
inch
•
10
-5
degree
•
PLS
Position droop
(deviation counter value)
2
PLS
M-codes
1
-
Torque limit value
1
%
Motor current
1
%
Motor rpm
2
r/min
Servo command value
2
PLS
Virtual servo motor feed
current value
2
PLS
Synchronous encoder current
value
2
PLS
Virtual servo M-code
1
-
Current value after main shaft
differential gear
2
PLS
Current value within one
revolution of cam axis
2
PLS
Executed cam No.
1
-
Executed stroke amount
2
10
-1
µ
m
•
10
-5
inch
•
PLS
Any address (fixed to 4 bytes)
2
-
Valid in SV22
virtual mode
only
(2) Modules and signals used
Input Module
Signal
Reading Timing
Number of Points Settable
A273EX
TRA
3
A172SENC
TRA
1
Sequencer input module
X device
0.8ms
8
(Note)
:
Only one PLC input module can be used.






























