65
Bump Testing MIDAS
®
A bump test is not intended to be an accurate calibration, but is used as a confidence check to ensure that the
gas detection system is functional. Since some of the target gases are difficult to handle, bump testing often
makes use of cross sensitivities so that more convenient gases can be used.
Equipment
The following items are required:
Test gas (see table)
Special regulator for extractive use (if using field calibration cylinder) or suitable sample bag (if not sampling
directly from cylinder)
Tubing (suitable for gas being applied)
Preparation
Most of the test gases are highly toxic. It is essential that personnel using these toxic gases be trained in their use.
Ensure that the test gas will be vented safely.
Applying test gas may cause alarm, fault or maintenance fault indications on the 4-20 mA loop, relays or digital
outputs. Before starting a test, ensure that suitable steps have been taken to prevent these indications from
triggering unwanted actions. The MIDAS
®
has a special mode for bump testing where the alarm outputs are
inhibited (see section 8.4.1).
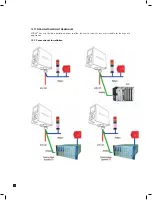
To test extractive systems we recommend the use of a gas sample bag and allow the extractive unit to draw a
sample of gas at its normal working flow rate. Suitable sample bags are available from SKC Inc. (www.skcinc.com).
Special regulators for extractive applications to use with field calibration cylinders are also available.
If non-PTFE-lined tube has to be used, response times may be longer than expected, especially when using
chlorine. In this case, it is especially important to keep the tubing short.
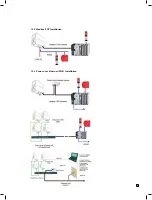
The pyrolyzer should be tested in the same way as an extractive system, but using NF
3
as the test gas. If NF
3
is not available, chlorine can be used at a concentration of 5 ppm. If using chlorine, the freon filter must be
removed from the unit before the test and replaced after the test.
NOTE: A test with chlorine operates the electrochemical cell and the unit’s electronics, but does not test the
pyrolyzer module itself.
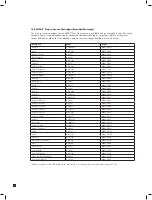
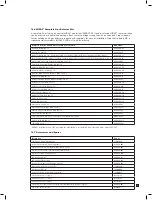
Target Gas
Formula
Cartridge
Part No.
Range (ppm)
Recommended
Bump Test Gas
Conc. (ppm)
Flow Rate
(cc/min)
Max. Time
Ammonia
NH
3
MIDAS-S-NH3
100
Ammonia
50
500
120
Arsine
AsH
3
MIDAS-S-ASH
0.2
Phosphine
0.5
500
120
Boron
Trichloride
BCl
3
MIDAS-S-HCl
8 C
hlorine
5 5
00
1
20
Boron
Trifluoride
BF
3
MIDAS-S-HFX
8 C
hlorine
5 5
00
1
20
Bromine
Br
2
MIDAS-S-BR2
0.4
Chlorine
Low
500
120
Carbon Dioxide
CO
2
MIDAS-S-CO2
2% v/v
Carbon Dioxide
2% v/v
500
120
Carbon
Monoxide
CO
MIDAS-S-COX
100
Carbon
Monoxide
100
500
120
Chlorine
Cl
2
MIDAS-S-HAL
2
Chlorine
2
500
120
Chlorine
Dioxide
ClO
2
MIDAS-S-BR2
0.4
Chlorine
Low
500
120
Chlorine
Trifluoride
ClF
3
MIDAS-S-SF4
0.
8
Chlorine
L
ow
5
00
1
20
Diborane
B
2
H
6
MIDAS-S-HYD
0.4
Phosphine
0.5
500
120
Dichlorosilane
SH
2
Cl
2
MIDAS-S-HCl
10
Chlorine
5
500
120
Disilane
Si
2
H
6
MIDAS-S-SHX
20
Hydrogen Sulfide
< 25
500
120
Fluorine
F
2
MIDAS-S-HAL
4
Chlorine
5
500
120
Germane
GeH
4
MIDAS-S-HYD
0.8
Phosphine
0.5
500
120
Hydrogen
H
2
(ppm)
MIDAS-S-H2X
1,000
Hydrogen
1000
500
120
Hydrogen
H
2
(%LEL)
MIDAS-S-LEL
100% LEL
Methane
500
120