855
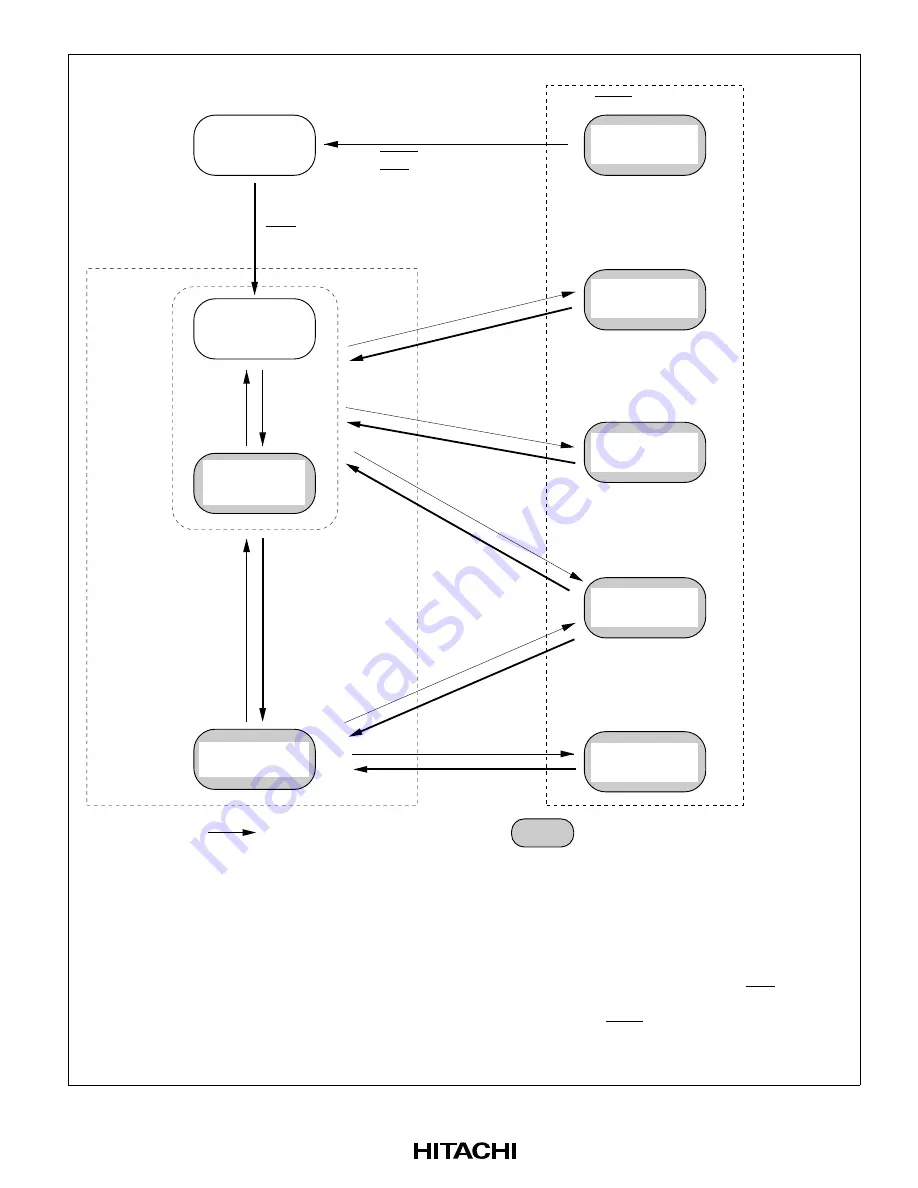
Program-halted state
Program execution state
SCK2 to
SCK0= 0
SCK2 to
SCK0
≠
0
SLEEP command
SSBY = 1, PSS = 1
DTON = 1, LSON = 1
Clock switching
exception processing
SLEEP command
SSBY = 1, PSS = 1
DTON = 1, LSON = 0
After the oscillation
stabilization time
(STS2 to 0), clock
switching exception
processing
SLEEP command
SLEEP
command
External
interrupt
*
4
Any interrupt
*
3
SLEEP
command
SLEEP
command
SLEEP command
Interrupt
*
2
LSON bit = 0
Interrupt
*
2
Interrupt
*
1
LSON bit = 1
STBY pin = High
RES pin = Low
STBY pin = Low
SSBY= 0, LSON= 0
SSBY= 1,
PSS= 0, LSON= 0
SSBY= 0,
PSS= 1, LSON= 1
SSBY= 1,
PSS= 1, DTON= 0
RES pin = High
: Transition after exception processing
: Low power dissipation mode
Reset state
High-speed mode
(main clock)
Medium-speed
mode
(main clock)
Sub-active mode
(subclock)
Sub-sleep mode
(subclock)
Hardware
standby mode
Software
standby mode
Sleep mode
(main clock)
Watch mode
(subclock)
Notes: 1.
2.
3.
4.
NMI, IRQ0 to IRQ7, and WDT1 interrupts
NMI, IRQ0 to IRQ7, IWDT0 interrupts, WDT1 interrupt, and TMR0 to TMR3 interrupts
All interrupts
NMI and IRQ0 to IRQ7
• When a transition is made between modes by means of an interrupt, the transition cannot be made
on interrupt source generation alone. Ensure that interrupt handling is performed after accepting the
interrupt request.
• From any state except hardware standby mode, a transition to the reset state occurs when RES is
driven Low.
• From any state, a transition to hardware standby mode occurs when STBY is driven low.
• Always select high-speed mode before making a transition to watch mode or sub-active mode.
Figure 24-1 Mode Transition Diagram