6 Configuration Mode Introduction
6.4 SSPI
UG290-2.5.2E
62(98)
6.4.4
Connection Diagram for SSPI Configuration Mode
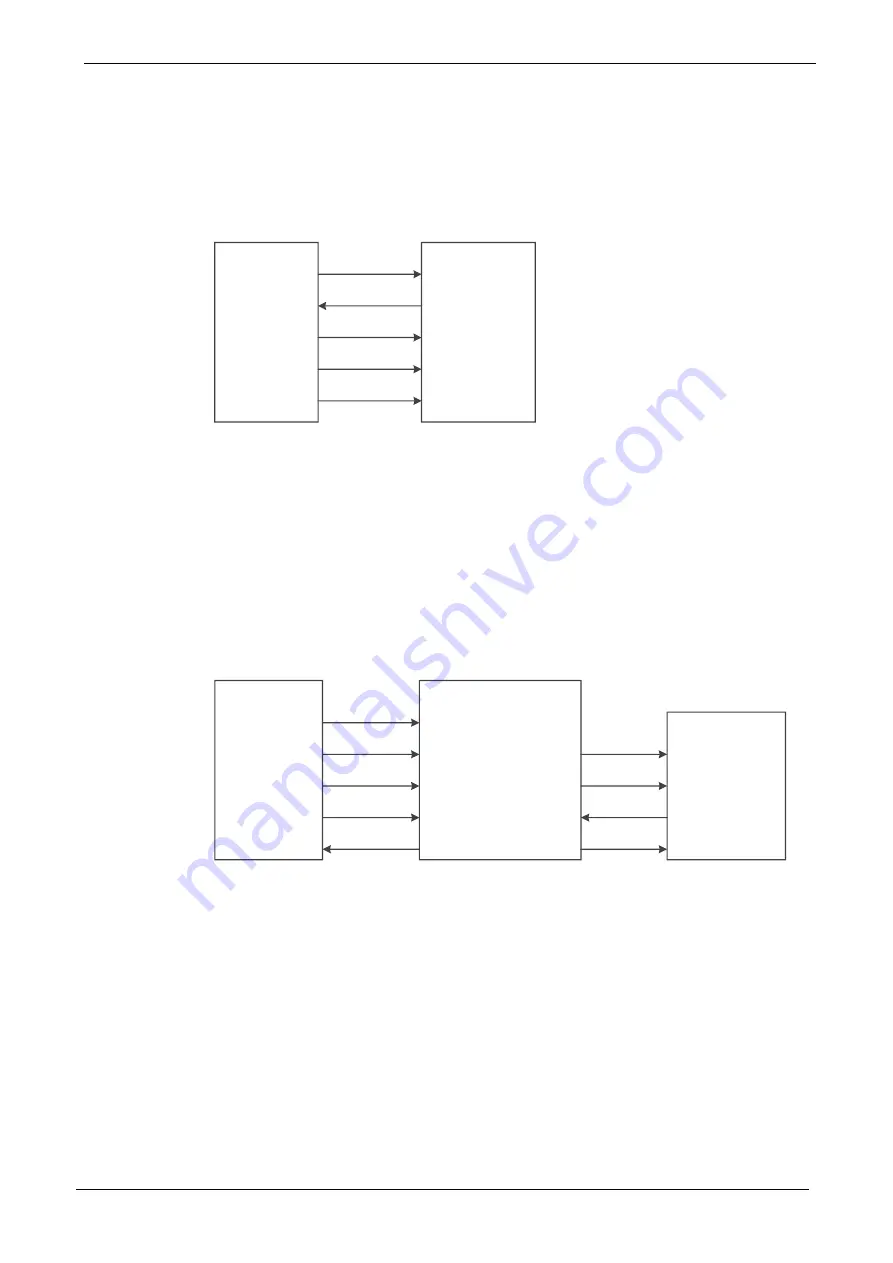
The connection diagram for configuring Gowin FPGA products via
SSPI is shown in Figure 6-37.
Figure 6-37 SSPI
Configuration Mode Connection Diagram
FPGA
SCLK
SO
SI
CLK_HOLDN
SSPI_CS_N
Host
CLK
DIN
DOUT
CTRL
CS_N
Note!
The figure above shows the minimum system diagram for the SSPI configuration. The
value of the SSPI MODE is "001". The connection of the other fixed pins is shown in
Figure 6-1.
In addition to SRAM, SSPI can be used to program external SPI Flash.
The MODE value of the Flash programming is the same as the MODE
value of SSPI configuration mode. Configuration data can be written to
SRAM or an external Flash using Gowin programmer. The connection
diagram for programming an external Flash via SSPI is shown in Figure
6-38.
Figure 6-38 Connection Diagram of Programming External Flash via SSPI
FPGA
CLKHOLD_N
SCLK MCLK
SSPI_CS_N MCS_N
SI MI
SO MO
Host
CTRL
CLK
CS_N
DOUT
DIN
Flash
CLK
CS_N
DOUT
DIN
Note!
All Arora family devices support programming external Flash via SSPI.
For the LittleBee
®
family devices, currently only GW1N(R)-9 supports programming
external Flash via SSPI.
Please refer to Figure 6-39 for the flow of programming external Flash
via SSPI.
First, send the "Program SPI Flash" (0x1600) instruction to FPGA via
SSPI. After this, the FPGA can forward SSPI to Flash, and the SSPI on the
Host side can directly access Flash. Then, it can be programmed according
to Flash timing.
Note that when reading data from Flash, the data being read back is
delayed by one bit. For example, when SSPI reads Flash's ID Code, it
needs to send an extra Clock to get the last bit.
















































