SAS Interface
1-4
C141-C012
1.1.2 Physical links and phys
A physical link is a set of four wires used as two differential signal pairs. One
differential signal transmits in one direction while the other differential signal
transmits in the opposite direction. Data may be transmitted in both directions
simultaneously.
A physical phy contains a transceiver which electrically interfaces to a physical
link, which attaches to another physical phy.
Phys are contained in ports. Phys interface to the service delivery subsystem.
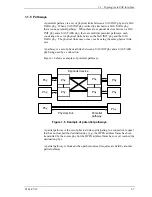
Figure 1.3 shows two phys attached with a physical link.
An attached phy is the phy to which a phy is attached over a physical link. A
device may contain one or more phys. Each phy has a phy identifier which is
unique within the device.
Phy
(Transceiver)
Physical link
Differential signal pair
Differential signal pair
Receiver
Transmitter
Phy
(Transceiver)
Transmitter
Receiver
Figure 1.3 Physical links and phys
1.1.3 Ports (narrow ports and wide ports)
A port contains one or more phys. Ports in a device are associated with physical
phys based on the identification sequence. A port is created from a set of physical
phys if one or more physical phys contained within a device:
a) transmit the same SAS address during the identification sequence; and
b) receive the same SAS address during the identification sequence (i.e., the
corresponding attached phy or phys transmit the same SAS address).
Summary of Contents for MAX3036RC SERIES
Page 4: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 128: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 136: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 338: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 368: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 378: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 380: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 394: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 396: ...This page is intentionally left blank ...
Page 398: ......
Page 399: ......
Page 400: ......