the same subnet, there is no route asymmetry dynamically. But if you configure the static route on
one DC and not on the other, there is asymmetry.
8.
If the port-channel specified in the
proxy-gateway
command is not a VLT LAG, the configuration
is rejected by the CLI. VLT LAG to a legacy LAG when it is part of proxy-gateway.
9.
You cannot change the LLDP port channel interface to a legacy LAG when you enable the proxy
gateway.
10. Dell recommends using the
vlt-peer-mac transmit
command only for square VLTs without
diagonal links.
11. VRRP and IPv6 routing is not supported.
12. Private VLANs (PVLANs) are not supported.
13. When a Virtual Machine (VM) moves from one VLT domain to the another VLT domain, the VM host
send the gratuitous ARP (GARP) , which in-turn triggers a mac movement from the previous VLT
domain to the newer VLT domain.
14. After a station move, if a host sends a TTL1 packet destined to its gateway; for example, a previous
VLT node, the packet may be dropped.
15. After a station move, if a host first PINGs its gateway; for example, a previous VLT node it results a 40
to 60% success rate considering it takes a longer path.
16. L3 frames can be received out-of-order at the L3 cloud when you remove and add back a MAC. This
can happen when proxy gateway routing and sub-optimal routing intersperse witth each other.
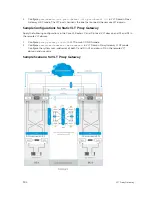
Enabling the VLT Proxy Gateway
To enable the VLT Proxy Gateway feature, the system mac addresses of C and D in the local VLT domain
must be installed in C1 and D1 in the remote VLT domain and vice versa. You can install the mac address
in two methods - the
proxy-gateway lldp
method or the
proxy-gateway static
configuration.
Proxy-gateway LLDP is a dynamic method of installing the local mac addresses in the remote VLT
domain, which is achieved using a new organizational TLV in LLDP packets.
The VLT proxy gateway can be configured in a VLT domain context using the cli command
proxy-
gateway LLDP
. You enter the proxy-gateway Configuration mode when you enter this command. The
port-channel interface of the square VLT link on which LLDP packets are to be sent is specified by
the
peer-domain-link port-channel
command.
Configuring the
proxy gateway lldp
and the
peer-domain-link
port channel, LLDP sets TLV flags
on the interfaces for receiving and transmitting private TLV packets. After defining these organizational
TLV settings, LLDP encodes the local system mac-addresses as organizational TLVs for transmitting to
the peer. If you specify the
no proxy gateway LLDP interface
command, LLDP stops transmitting
and receiving proxy gateway TLV packets on the specified interfaces. However, other TLVs are not
affected. From the interfaces on which proxy gateway LLDP is enabled, LLDP decodes TLV packets from
the remote LLDP by using the new organizational TLV.
The following requirements must be satisfied for LLDP proxy gateway to function correctly:
• As LLDP is a direct link protocol, data centers must be directly connected.
• LLDP has a limited TLV size. As a result, information that is carried by this new TLV is limited to only
one or two MAC addresses.
• You must ensure proper configuration and physical setup on all related systems.
902
VLT Proxy Gateway
Summary of Contents for Z9000
Page 1: ...Dell Configuration Guide for the Z9000 System 9 7 0 0 ...
Page 80: ...grub reboot 80 Management ...
Page 128: ... 0 Te 1 1 Te 1 2 rx Flow N A N A 128 Access Control Lists ACLs ...
Page 491: ...Figure 70 Configuring OSPF and BGP for MSDP Multicast Source Discovery Protocol MSDP 491 ...
Page 496: ...Figure 73 MSDP Default Peer Scenario 1 496 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol MSDP ...
Page 497: ...Figure 74 MSDP Default Peer Scenario 2 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol MSDP 497 ...
Page 498: ...Figure 75 MSDP Default Peer Scenario 3 498 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol MSDP ...
Page 760: ...Figure 100 Single and Double Tag TPID Match 760 Service Provider Bridging ...
Page 761: ...Figure 101 Single and Double Tag First byte TPID Match Service Provider Bridging 761 ...