6.
Enable the VLAN.
INTERFACE VLAN mode
no shutdown
7.
To obtain maximum VLT resiliency, configure the PVLAN IDs and mappings to be identical on both
the VLT peer nodes. Set the PVLAN mode of the selected VLAN to primary.
INTERFACE VLAN mode
private-vlan mode primary
8.
Map secondary VLANs to the selected primary VLAN.
INTERFACE VLAN mode
private-vlan mapping secondary-vlan
vlan-list
The list of secondary VLANs can be:
• Specified in comma-delimited (
VLAN-ID,VLAN-ID
) or hyphenated-range format (
VLAN-ID-
VLAN-ID
).
• Specified with this command even before they have been created.
• Amended by specifying the new secondary VLAN to be added to the list.
Proxy ARP Capability on VLT Peer Nodes
The proxy ARP functionality is supported on VLT peer nodes.
A proxy ARP-enabled device answers the ARP requests that are destined for another host or router. The
local host forwards the traffic to the proxy ARP-enabled device, which in turn transmits the packets to the
destination.
By default, proxy ARP is enabled. To disable proxy ARP, use the
no proxy-arp
command in the interface
mode. To re-enable proxy ARP, use the
ip proxy-arp
command in INTERFACE mode. To view if proxy
ARP is enabled on the interface, use the
show config
command in INTERFACE mode. If it is not listed in
the
show config
command output, it is enabled. Only nondefault information is displayed in the
show
config
command output.
ARP proxy operation is performed on the VLT peer node IP address when the peer VLT node is down. The
ARP proxy stops working either when the peer routing timer expires or when the peer VLT node goes up.
Layer 3 VLT provides a higher resiliency at the Layer 3 forwarding level. VLT peer routing enables you to
replace VRRP with routed VLT to route the traffic from Layer 2 access nodes. With proxy ARP, hosts can
resolve the MAC address of the VLT node even when VLT node is down.
If the ICL link is down when a VLT node receives an ARP request for the IP address of the VLT peer, owing
to LAG-level hashing algorithm in the top-of-rack (TOR) switch, the incorrect VLT node responds to the
ARP request with the peer MAC address. Proxy ARP is not performed when the ICL link is up and the ARP
request the wrong VLT peer. In this case, ARP requests are tunneled to the VLT peer.
Proxy ARP supported on both VLT interfaces and non-VLT interfaces. Proxy ARP supported on symmetric
VLANs only. Proxy ARP is enabled by default. Routing table must be symmetrically configured to support
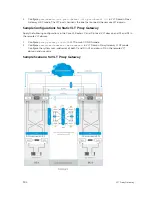
proxy ARP. For example, consider a sample topology in which VLAN 100 is configured on two VLT nodes,
node 1 and node 2. ICL link is not configured between the two VLT nodes. Assume that the VLAN 100 IP
address in node 1 is 10.1.1.1/24 and VLAN 100 IP address in node 2 is 20.1.1.2/24. In this case, if the ARP
request for 20.1.1.1 reaches node 1, node 1 will not perform the ARP request for 20.1.1.2. Proxy ARP is
Virtual Link Trunking (VLT)
893
Summary of Contents for Z9000
Page 1: ...Dell Configuration Guide for the Z9000 System 9 7 0 0 ...
Page 80: ...grub reboot 80 Management ...
Page 128: ... 0 Te 1 1 Te 1 2 rx Flow N A N A 128 Access Control Lists ACLs ...
Page 491: ...Figure 70 Configuring OSPF and BGP for MSDP Multicast Source Discovery Protocol MSDP 491 ...
Page 496: ...Figure 73 MSDP Default Peer Scenario 1 496 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol MSDP ...
Page 497: ...Figure 74 MSDP Default Peer Scenario 2 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol MSDP 497 ...
Page 498: ...Figure 75 MSDP Default Peer Scenario 3 498 Multicast Source Discovery Protocol MSDP ...
Page 760: ...Figure 100 Single and Double Tag TPID Match 760 Service Provider Bridging ...
Page 761: ...Figure 101 Single and Double Tag First byte TPID Match Service Provider Bridging 761 ...