Aespire View
10-14
M1132382
Ventilator theory
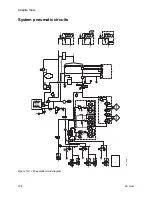
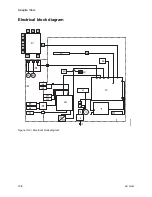
The ventilator pneumatics are located in the rear of the breathing
system. A precision flow valve controls gas flow to the patient. During
inspiration, this gas flow closes the exhalation valve and pushes the
bellows down. During expiration, a small flow pressurizes the
exhalation diaphragm to supply PEEP pressure.
Volume measurements come from flow sensors in the flow sensor
module. Two tubes from each sensor connect to a transducer. The
transducer measures the pressure change across each sensor,
which changes with the flow. A third pressure transducer measures
airway pressures at the inspiratory flow sensor.
The ventilator uses data from the flow sensors for volume-related
numerics and alarms. The ventilator also uses the flow sensors to
adjust its output for changes in fresh gas flow and small leaks in the
breathing system.
In volume ventilation modes, certain alarm conditions prevent the
automatic adjustment of ventilator delivery based on measured flow
values. In these cases, the ventilator may not be able to deliver within
the accuracy range specified. If compensation stops for a number of
breaths, the condition causing the hold shows as an alarm. Automatic
volume compensation resumes when alarm conditions are resolved.
For better precision a small quantity of gas bleeds through a resistor
to help keep the pressure on the exhalation valve constant. At high
airway pressures, this can cause a slight hiss during inspiration.
WARNING
Do not try to silence the pneumatic resistor. If it is
blocked, the ventilator can malfunction and cause patient
injury.
Summary of Contents for Aespire View
Page 1: ...Aespire View User s Reference Manual Software Revision 6 X...
Page 16: ...Aespire View 1 8 M1132382...
Page 46: ...Aespire View 3 16 M1132382...
Page 50: ...Aespire View 4 4 M1132382...
Page 88: ...Aespire View 7 8 M1132382...
Page 112: ...Aespire View 9 10 M1132382...
Page 148: ...Aespire View I 4 M1132382...