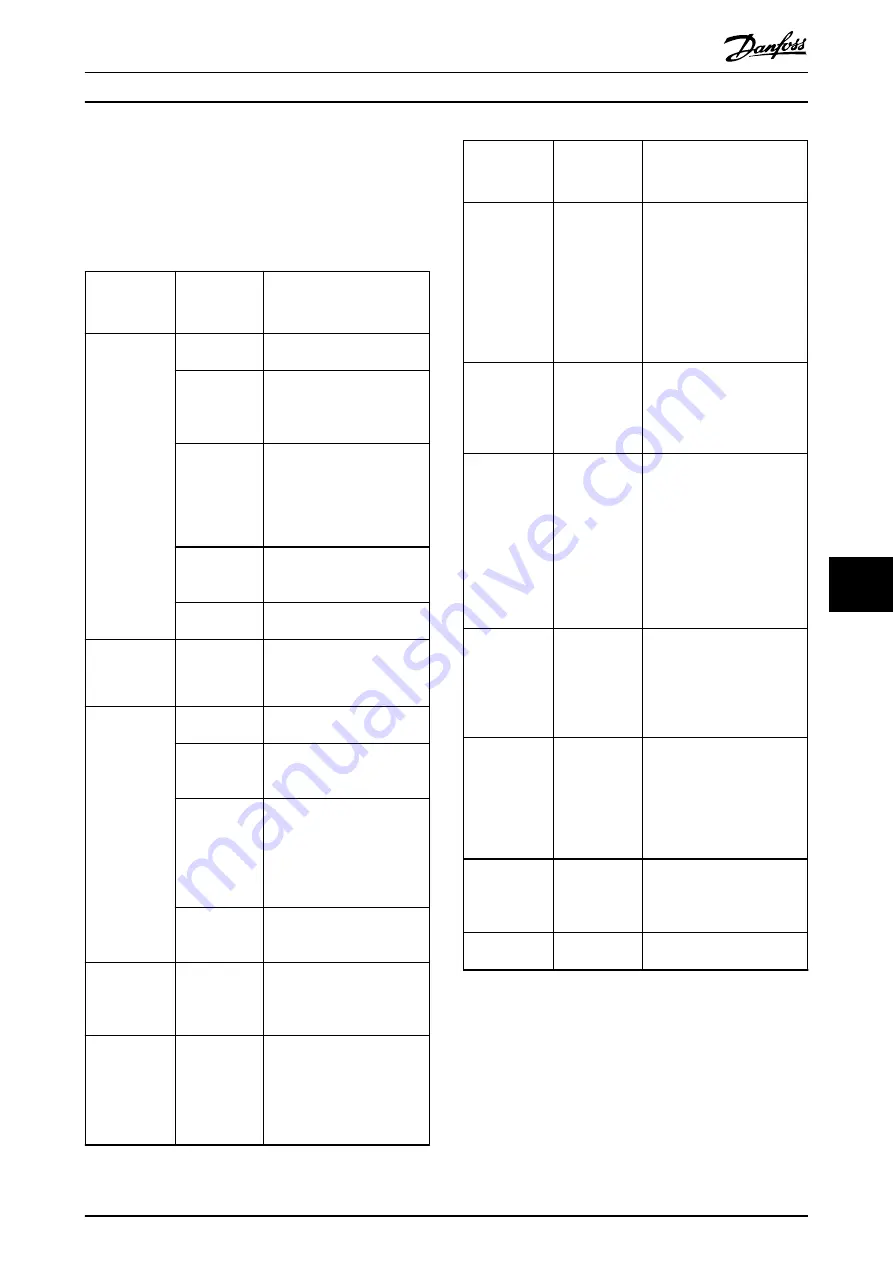
9.3 Servo Access Box (SAB)
9.3.1 Troubleshooting
lists potential faults on the SAB, their possible
causes, and actions for correcting the faults.
Fault
Possible cause Possible solution
LCP display
dark or has no
function.
Missing input
power.
Check the input power source.
Missing or
open fuses or
circuit breaker
tripped.
Check the fuses and circuit
breaker.
No power to
the LCP.
•
Check the LCP cable for
proper connection or
damage.
•
Replace any faulty LCP or
connection cables.
Incorrect
contrast
setting.
Press [Status] + [
▲
]/[
▼
] to
adjust the contrast.
Display is
defective.
Replace the faulty LCP or
connection cable.
Open power
fuses or circuit
breaker trip.
Phase-to-phase
short.
•
Check the cabling.
•
Check for loose
connections.
DC-link voltage
too high.
Brake resistor
not connected.
Check the brake resistor
cabling.
Brake resistor
too high
resistance.
Check if the lowest resistance
value has been entered.
Several servo
drives are
decelerating
with
insufficient
ramp time.
•
Avoid simultaneous
deceleration of several
servo drives.
•
Change the deceleration
speed of the servo drives.
Brake resistor
functionality
not activated.
Activate the brake function.
DC-link voltage
too low.
Incorrect mains
supply.
Check supply voltage matches
the allowed specification
detailed in
DC overcurrent. The sum of the
servo drive
current exceeds
the maximum
rating of the
SAB.
•
Check the servo drive
current consumption.
•
Avoid simultaneous
acceleration of all servo
drives.
Fault
Possible cause Possible solution
U
AUX
overcurrent.
The servo
drives are
consuming
more power on
the U
AUX
line
than allowed.
•
Check the number of
attached servo drives with
the shell diagrams in the
VLT
®
Integrated Servo Drive
ISD
®
510 System Design
Guide.
•
Avoid simultaneous lifting
of the servo drive brakes.
U
AUX
overvoltage.
Incorrect U
AUX
supply.
Check that the supply
matches the allowed specifi-
cation detailed in
chapter 5.6 Auxiliary Supply
Requirements
U
AUX
undervoltage.
Incorrect U
AUX
supply.
•
Check that the supply
voltage matches the
allowed specification
detailed in
chapter 5.6 Auxiliary Supply
Requirements
•
Check that the output
power of the supply is
sufficient.
Mains phase
loss.
A phase is
missing on the
supply side, or
the voltage
imbalance is
too high.
Check the supply voltages and
supply currents to the SAB.
Grounding fault. Grounding
fault.
•
Check for proper
grounding and loose
connections.
•
Check the hybrid cables
for short circuits or
leakage currents.
Brake resistor
error.
Faulty brake
resistor.
Remove the power to the
SAB, wait for the discharge
time to elapse then replace
the brake resistor.
Brake chopper
error.
Faulty brake
chopper.
Check the setting in
parameter
2-15 Brake Check
.
Table 9.3 Troubleshooting SAB
Diagnostics
Operating Instructions
MG75K102
Danfoss A/S © 12/2015 All rights reserved.
77
9
9






























