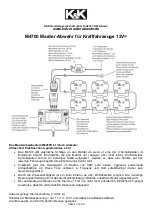
www.balluff.com
17
english
6
P interface
6.1
Principle
The P interface is a universal pulse interface and unifies the
functions of the falling and rising edges. The position
measuring system control is done via Init and start/stop
signals. Here, the “start pulse” is the reference point for the
travel time measurement.
Reliable signal transmission, even with cable lengths of up
to 500 m between the evaluation unit and BTL is ensured
by the particularly fail-safe RS485 differential driver and
receiver. Interfering signals are effectively suppressed.
DPI/IP is a protocol for direct data exchange between the
controller and BTL. Here, the signal lines transmit
additional information, such as manufacturer, sensor type,
measuring length, and waveguide velocity. This makes it
possible to start up or exchange a BTL without needing to
manually change the control parameters.
The interface enables bi-directional communication and
includes integrated diagnostic functions. Downtimes are
reduced thanks to Plug & Play and automatic
parameterization.
6.2
DPI/IP method
6.2.1 Function and characteristics
The DPI/IP method includes two operating modes, DPI
measuring operation and operation with the IP data
protocol.
DPI = digital pulse interface
IP = integrated protocol
DPI measuring operation
The Init pulse is sent to the BTL via the Init line at regular
intervals, its rising edge triggers a measurement.
Fig. 6-1:
Start
T
Init
T
Stop
T
Init
Start/Stop
Principle of data transfer in DPI measuring operation
T
Init
1 μs to 5 μs
T
Start
3 μs to 5 μs (typ. 4 µs)
T
Stop
3 μs to 5 μs (typ. 4 µs)
Operation with IP data protocol
If the length of the Init pulse T
IP
is extended to 10 μs to
50 μs, the BTL switches from DPI measuring mode to
operation with the IP data protocol (see Fig. 6-1).
Here, a character string (command) is transferred to the
BTL after the Init pulse. While the start pulse is still sent by
the BTL as a response on the start/stop line, a character
string (response) is transferred to the controller instead of
the stop pulses, which contains the requested response
dependent on the command.
Each character in the transfer protocol has the following bit
structure:
…
Start Bit0 Bit1 Bit2
Bit6 Bit7 PBit Stop
Bit
T
Start bit
Start-of-frame bit
Bit 0 to bit 7
8 data bits
PBit
Parity bit (even parity)
Stop
Stop-of-frame bit
T
Bit
4 μs (bit length at a data rate of
250 kbit/s)
Data security during transfer of the string is achieved with
the parity and CRC16 checks with polynomial
X16+X12+X5+1 (corresponds to 0x1021). If there is a
transfer or protocol error, the BTL sends an appropriate
error message as the response.
Fig. 6-2:
T
D1
Command
Response
T
IP
Start
T
Init
Start/Stop
…
…
Principle of data transfer with the IP data protocol
T
IP
10 μs to 50 μs
Operation with IP data protocol
Command
Command to request BTL data
(information that is stored in the BTL)
T
Start
3 μs to 5 μs (typ. 4 µs)
T
D1
> 50 μs
Response
Response in line with the request
Alternative: error message
BTL7-P511-M _ _ _ _ -J-DEXC-TA12
Magnetostrictive Linear Position Sensor – Rod Style
Ignition protection “d”
Flameproof enclosure
Summary of Contents for BTL7-P511-M J-DEXC-TA12 Series
Page 2: ...www balluff com...
Page 14: ...www balluff com...
Page 38: ...www balluff com...
Page 62: ...www balluff com...
Page 86: ...www balluff com...
Page 110: ...www balluff com...
Page 134: ...www balluff com...
Page 148: ...16 5 1 1 2 3 BTL BTL 5 2 BTL BTL 5 BTL7 P511 M_ _ _ _ J DEXC TA12 d...
Page 158: ...www balluff com...
Page 172: ...16 5 1 1 2 3 BTL BTL 5 2 BTL BTL 5 BTL7 P511 M_ _ _ _ J DEXC TA12 d...
Page 181: ......