Network Connections to Modbus and
Direct
NET
Configuring Port 2 For
D
Diirreecctt
NET
This section describes how to configure the CPU’s built-in networking ports for either
Modbus or
Direct
NET. This will allow you to connect the DL205 PLC system directly to
Modbus networks using the RTU protocol, or to other devices on a
Direct
NET network. For
more details on
Direct
NET, order our
Direct
NET manual, part number DA–DNET–M.
Configuring Port 2 For Modbus RTU
Modbus hosts system on the network must be capable of issuing the Modbus commands to
read or write the appropriate data. For details on the Modbus protocol, please refer to the
Gould Modbus Protocol reference Guide (P1–MBUS–300 Rev. J). In the event a more recent
version is available, check with your Modbus supplier before ordering the documentation.
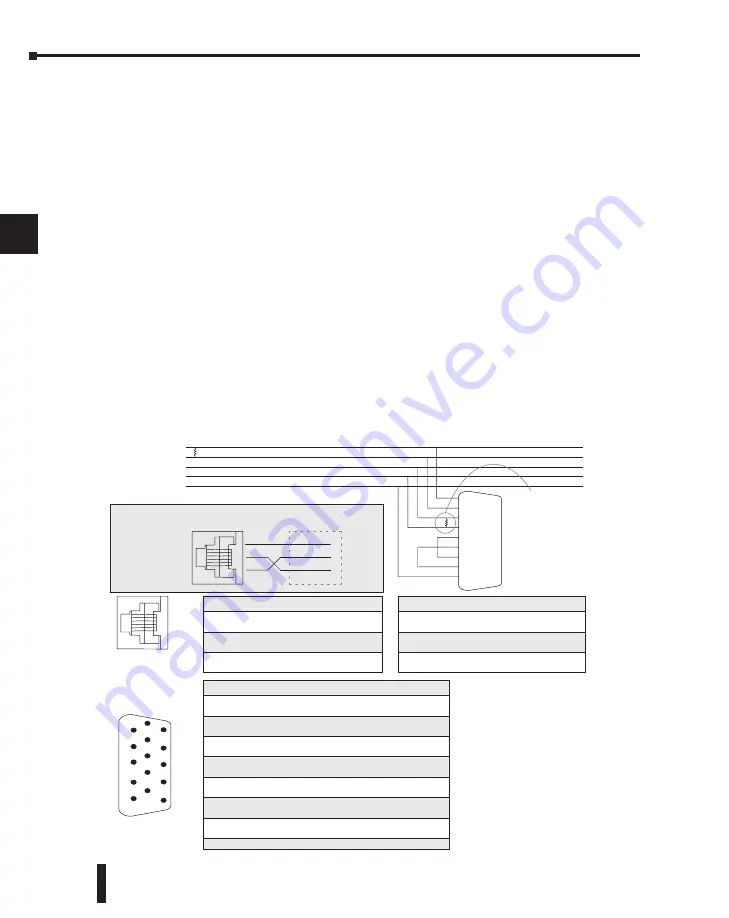
You will need to determine whether the network connection is a 3-wire RS–232 type, or a 5-
wire RS–422 type. Normally, the RS–232 signals are used for shorter distance (15 meters
max) communications between two devices. RS–422 signals are for longer distance (1000
meters max.) multi-drop networks (from 2 to 247 devices). Use termination resistors at both
ends of RS–422 network wiring, matching the impedance rating of the cable (between 100
and 500 ohms).
DL205 User Manual, 4th Edition, Rev. B
Chapter 4: System Design and Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
A
B
C
D
RXD+
RXD–
TXD+
TXD–
Signal GND
TXD
RXD
RS–422
Multi–drop
Network
RS–232
Point-to-point
DTE Device
4
3
1
PORT 2
(DL250–1, DL260)
RS–422 Slave
9 TXD+
10 TXD–
13 RXD+
6 RXD–
1 1 R TS+
12 R TS–
14 CTS+
15 CTS–
7 0
V
PC/PLC Master
PORT 1: DL250–1, DL260 (slave only)
PORT 2: DL240 (slave only)
T ermination
Resistor on
last slave only
0V Signal
GND
RXD
TXD
RS–232
Master
Port 1 Pinouts (DL250–1 / DL260)
1
0 V
Power (–) connection (GND)
2
5 V
Power (+) conection
3 RXD Receive
Data
(RS-232)
4
TXD T ransmit Data (RS-232)
5
5 V
Power (+) conection
6
0 V
Power (–) connection (GND)
6-pin Female
Modular Connector
Port 2 Pin Descriptions (DL240 only)
1
0 V
Power (–) connection (GND)
2
5 V
Power (+) conection
3 RXD Receive
Data
(RS-232)
4
TXD T ransmit Data (RS-232)
5
R TS Request
to
Send
6
0 V
Power (–) connection (GND)
15-pin Female
D-Sub connector
The recommended cable
for RS-232 or RS-422 is
AutomationDirect L19772
(Belden 8102) or equivalent.
The recommended cable for
RS-485 is AutomationDirect L19827
(Belden 9841) or equivalent.
Port 2 Pin Descriptions (DL250–1 / DL260)
1
5 V
5 VDC
2 TXD2 T ransmit Data (RS-232)
3 RXD2 Receive
Data
(RS-232)
4 R TS2 Ready to Send (RS–232)
5 CTS2 Clear to Send (RS–232)
6 RXD2– Receive Data – (RS–422) (RS–485 DL260)
7
0 V
Logic Ground
8
0 V
Logic Ground
9 TXD2+ T ransmit Data + (RS–422) (RS–485 DL260)
10 TXD2
– T ransmit Data – (RS–422) (RS–485 DL260)
1 1 R TS2 + Request to Send + (RS–422) (RS–485 DL260)
12 R TS2 – Request to Send – (RS–422)(RS–485 DL260)
13 RXD2
+ Receive Data + (RS–422) (RS–485 DL260)
14 CTS2 + Clear to Send + (RS422) (RS–485 DL260)
15 CTS2 – Clear to Send – (RS–422) (RS–485 DL260)
Note: The DL260 supports
RS–485 multi–drop net-
working. See the Network
Master Operation (DL260
Only) section later in this
chapter for details.
1
6
11
5
10
15
230
2
4
0
2
5
0
-1
2
6
0
ý
þ
þ
þ
ý
ý
þ
þ
230
240
2
5
0
-1
2
6
0
4–32
















































