2.
Insert cable gland suitable for connecting cable.
Information: When selecting cable glands observe type of protection (with Ex e
bzw. Ex d approval) and type of protection IP (refer to name plate).
➥
The enclosure protection IP stated on the name plate is only ensured if suitable
cable glands are used.
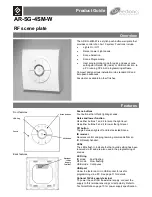
Figure 26: Name plate, example with enclosure protection IP68
5.3.1.2. Motor cables: connect
Table 14:
Terminal cross sections and terminal tightening torques
Tightening torques
Terminal cross sections
Speed
Type
2.0 Nm
0.5 – 16 mm
2
4 – 22
SAEx 25.1
SAREx 25.1
3.5 Nm
2.5 – 35 mm
2
32 – 90
1.2 – 2.4 Nm
4 – 16 mm
2
4 – 22
SAEx 30.1
SAREx 30.1
4.0 – 5.0 Nm
10 – 35 mm
2
32 – 45
6.0 – 12 Nm
16 – 70 mm
2
63 – 90
1.2 – 2.4 Nm
4 – 16 mm
2
4 – 5.6
SAEx 35.1
4.0 – 5.0 Nm
10 – 35 mm
2
8 – 22
6.0 – 12 Nm
16 – 70 mm
2
32 – 45
4.0 – 5.0 Nm
10 – 35 mm
2
4 – 11
SAEx 40.1
6.0 – 12 Nm
16 – 70 mm
2
16 – 32
1.
Remove cable sheathing and insert the wires into the cable glands.
2.
Fasten cable gland with the specified torque to ensure required enclosure pro-
tection.
3.
Strip wires.
4.
For flexible cables: Use end sleeves according to DIN 46228.
5.
Connect cables according to order-related wiring diagram.
In case of a fault: Hazardous voltage while protective earth conductor is NOT
connected!
Risk of electric shock.
→
Connect all protective earth conductors.
→
Connect PE connection to external protective earth conductor of connecting
cables.
→
Start running the device only after having connected the protective earth con-
ductor.
6.
Firmly tighten protective earth to PE connection (symbol:
).
7.
For shielded cables: Link the cable shield end via the cable gland to the housing
(earthing).
29
SAEx 25.1 – SAEx 40.1 / SAREx 25.1 – SAREx 30.1
ACExC 01.2
Electrical connection