Telnet Connection Establishment
109
[4200G-ui-vty0]
user privilege level 2
8
Configure Telnet protocol is supported.
[4200G-ui-vty0]
protocol inbound telnet
9
Set the maximum number of lines the screen can contain to 30.
[4200G-ui-vty0]
screen-length 30
10
Set the maximum number of commands the history command buffer can store to 20.
[4200G-ui-vty0]
history-command max-size 20
11
Set the timeout time to 6 minutes.
[4200G-ui-vty0]
idle-timeout 6
Telnet Connection
Establishment
Telneting to a Switch
from a Terminal
You can Telnet to a switch and then to configure the switch if the interface of the
management VLAN of the switch is assigned an IP address. To assign an IP address to
the interface of the management VLAN of a switch, you can log into the switch
through its Console port, enter VLAN interface view, and execute the
ip address
command.
Following are procedures to establish a Telnet connection to a switch:
1
Configure the user name and password for Telnet on the switch. Refer to “Telnet
Configuration with Authentication Mode Being None”, “Telnet Configuration with
Authentication Mode Being Password”, and “Telnet Configuration with
Authentication Mode Being Scheme” for more.
2
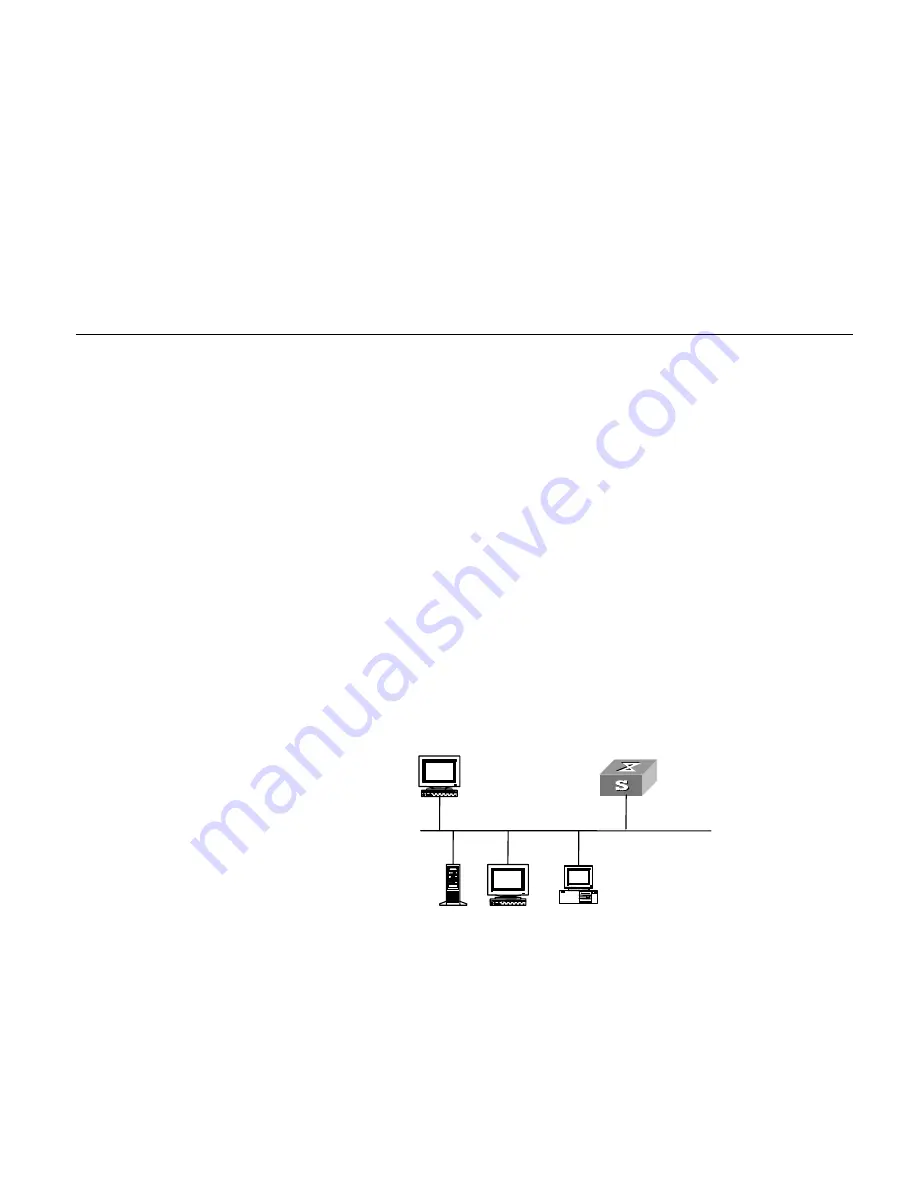
Connect your PC to the Switch, as shown in Figure 33. Make sure the Ethernet port
to which your PC is connected belongs to the management VLAN of the switch and
the route between your PC and the switch is available.
Figure 33
Network diagram for Telnet connection establishment
3
Launch Telnet on your PC, with the IP address of the management VLAN interface of
the switch as the parameter, as shown in Figure 34.
Workstation
Workstation
Server
PC w ith Telnet
running on it
(used to configure
the sw itch)
Ethernet port
Ethernet
Workstation
Workstation
Server
PC w ith Telnet
running on it
(used to configure
the sw itch)
Ethernet port
Ethernet
Summary of Contents for 4200G 12-Port
Page 10: ...8 CONTENTS...
Page 14: ...4 ABOUT THIS GUIDE...
Page 46: ...32 CHAPTER 5 LOGGING IN THROUGH WEB BASED NETWORK MANAGEMENT SYSTEM...
Page 48: ...34 CHAPTER 6 LOGGING IN THROUGH NMS...
Page 60: ...46 CHAPTER 9 VLAN CONFIGURATION...
Page 64: ...50 CHAPTER 10 MANAGEMENT VLAN CONFIGURATION...
Page 80: ...66 CHAPTER 13 GVRP CONFIGURATION...
Page 98: ...84 CHAPTER 15 LINK AGGREGATION CONFIGURATION...
Page 112: ...98 CHAPTER 18 MAC ADDRESS TABLE MANAGEMENT...
Page 126: ...112 CHAPTER 19 LOGGING IN THROUGH TELNET...
Page 162: ...148 CHAPTER 20 MSTP CONFIGURATION...
Page 274: ...260 CHAPTER 29 IGMP SNOOPING CONFIGURATION...
Page 276: ...262 CHAPTER 30 ROUTING PORT JOIN TO MULTICAST GROUP CONFIGURATION...
Page 298: ...284 CHAPTER 33 SNMP CONFIGURATION...
Page 304: ...290 CHAPTER 34 RMON CONFIGURATION...
Page 338: ...324 CHAPTER 36 SSH TERMINAL SERVICES...
Page 356: ...342 CHAPTER 38 FTP AND TFTP CONFIGURATION...
Page 365: ...Information Center Configuration Example 351 S4200G terminal logging...
Page 366: ...352 CHAPTER 39 INFORMATION CENTER...
Page 378: ...364 CHAPTER 40 BOOTROM AND HOST SOFTWARE LOADING...
Page 384: ...370 CHAPTER 41 Basic System Configuration and Debugging...
Page 388: ...374 CHAPTER 43 NETWORK CONNECTIVITY TEST...
Page 406: ...392 CHAPTER 45 CONFIGURATION OF NEWLY ADDED CLUSTER FUNCTIONS...