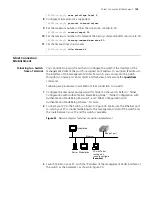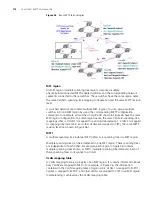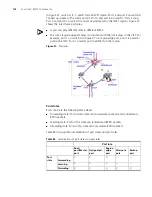
Telnet Configuration with Authentication Mode Being None
101
Note that if you configure not to authenticate the users, the command level available
to users logging into a switch depends on both the
authentication-mode
{
password
|
scheme
|
none
} command and the
user privilege level
level
command, as listed in Table 78.
Configuration
Example
Network requirements
Assume that you are a level 3 AUX user and want to perform the following
configuration for Telnet users logging into VTY 0:
Do not authenticate users logging into VTY 0.
Commands of level 2 are available to users logging into VTY 0.
Telnet protocol is supported.
The screen can contain up to 30 lines.
The history command buffer can contain up to 20 commands.
The timeout time of VTY 0 is 6 minutes.
Set the history
command buffer size
history-command max-size
value
Optional
The default history command buffer
size is 10. That is, a history
command buffer can store up to 10
commands by default.
Set the timeout time of
the VTY user interface
idle-timeout
minutes
[
seconds
]
Optional
The default timeout time of a user
interface is 10 minutes.
With the timeout time being 10
minutes, the connection to a user
interface is terminated if no
operation is performed in the user
interface within 10 minutes.
You can use the
idle-timeout
0
command to disable the timeout
function.
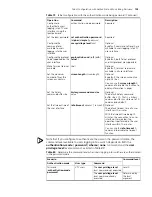
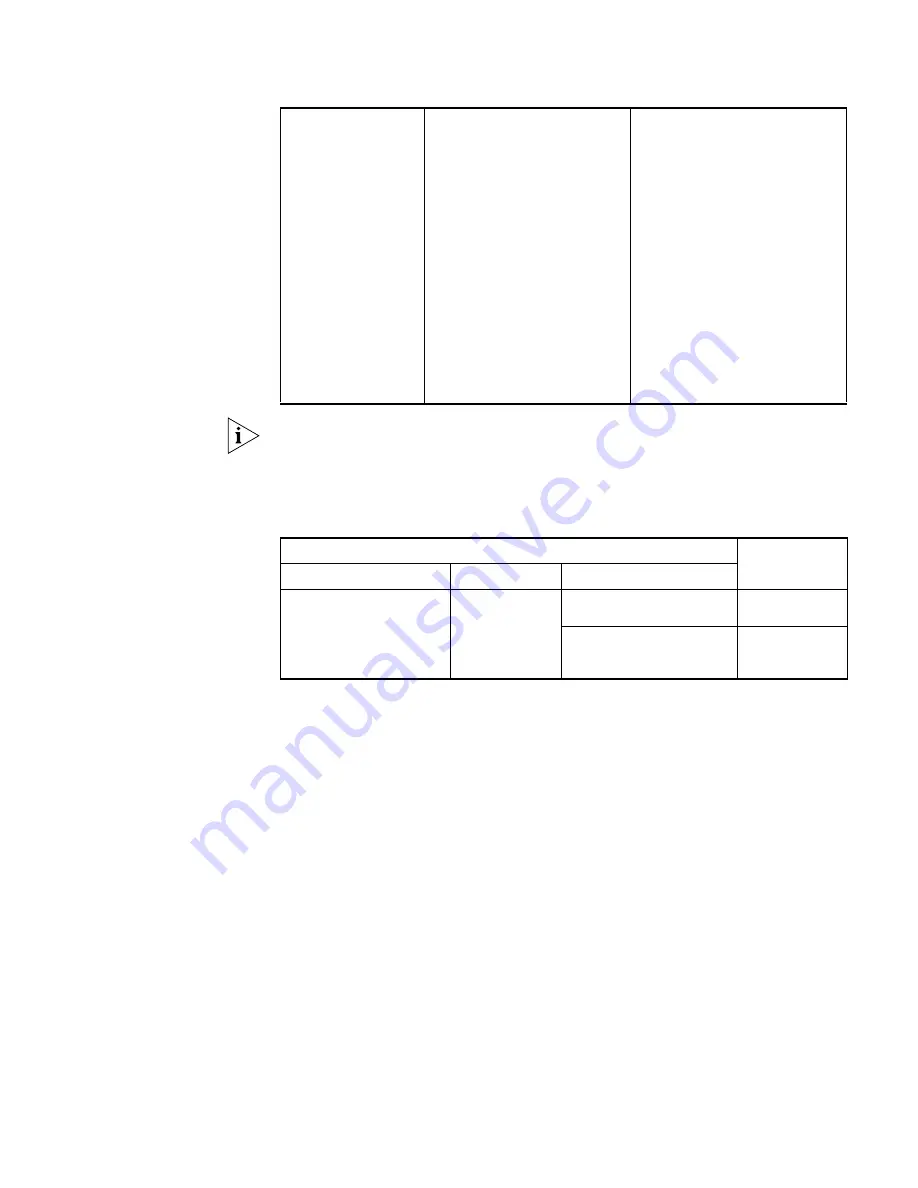
Table 78
Determine the command level when users logging into switches are not
authenticated
Scenario
Command level
Authentication mode
User type
Command
None
(
authentication-mode
none
)
VTY users
The
user privilege level
level
command not executed
Level 0
The
user privilege level
level
command already
executed
Determined by
the
level
argument
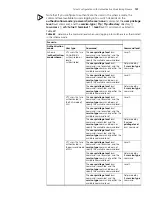
Table 77
Telnet configuration with the authentication mode being none
Operation
Command
Description
Summary of Contents for 4200G 12-Port
Page 10: ...8 CONTENTS...
Page 14: ...4 ABOUT THIS GUIDE...
Page 46: ...32 CHAPTER 5 LOGGING IN THROUGH WEB BASED NETWORK MANAGEMENT SYSTEM...
Page 48: ...34 CHAPTER 6 LOGGING IN THROUGH NMS...
Page 60: ...46 CHAPTER 9 VLAN CONFIGURATION...
Page 64: ...50 CHAPTER 10 MANAGEMENT VLAN CONFIGURATION...
Page 80: ...66 CHAPTER 13 GVRP CONFIGURATION...
Page 98: ...84 CHAPTER 15 LINK AGGREGATION CONFIGURATION...
Page 112: ...98 CHAPTER 18 MAC ADDRESS TABLE MANAGEMENT...
Page 126: ...112 CHAPTER 19 LOGGING IN THROUGH TELNET...
Page 162: ...148 CHAPTER 20 MSTP CONFIGURATION...
Page 274: ...260 CHAPTER 29 IGMP SNOOPING CONFIGURATION...
Page 276: ...262 CHAPTER 30 ROUTING PORT JOIN TO MULTICAST GROUP CONFIGURATION...
Page 298: ...284 CHAPTER 33 SNMP CONFIGURATION...
Page 304: ...290 CHAPTER 34 RMON CONFIGURATION...
Page 338: ...324 CHAPTER 36 SSH TERMINAL SERVICES...
Page 356: ...342 CHAPTER 38 FTP AND TFTP CONFIGURATION...
Page 365: ...Information Center Configuration Example 351 S4200G terminal logging...
Page 366: ...352 CHAPTER 39 INFORMATION CENTER...
Page 378: ...364 CHAPTER 40 BOOTROM AND HOST SOFTWARE LOADING...
Page 384: ...370 CHAPTER 41 Basic System Configuration and Debugging...
Page 388: ...374 CHAPTER 43 NETWORK CONNECTIVITY TEST...
Page 406: ...392 CHAPTER 45 CONFIGURATION OF NEWLY ADDED CLUSTER FUNCTIONS...