266
C
HAPTER
32: C
LUSTER
C
ONFIGURATION
HGMP V2 provides the following functions:
■
Topology discovery: HGMP V2 implements NDP (neighbor discovery protocol) to
discover the information about the directly connected neighbor devices, including
device type, software/hardware version, connecting port and so on. The
information such as device ID, port mode (duplex or half duplex), product version,
and BootROM version can also be given.
■
Topology information collection: HGMP V2 implements NTDP (neighbor topology
discovery protocol) to collect the information about device connections and
candidate devices within a specified hop range.
■
Member recognition: A management device can locate and recognize the member
devices in the cluster and then deliver configuration and management commands
to them.
■
Member management: You can add a device to a cluster or remove a device from
a cluster on the management device. You can also configure management device
authentication and handshake interval for a member device on the management
device.
Cluster-related configurations are described in the following sections.
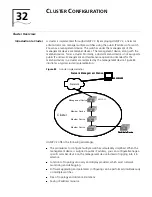
Cluster Roles
According to their functions and status in a cluster, switches in the cluster play
different roles. You can specify the role a switch plays. A switch also changes its role
according to specific rules.
Following three cluster roles exist: management device, member device, and
candidate device.
Figure 84 shows the role changing rule.
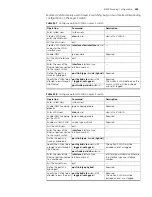
Table 234
Cluster role
Role
Configurations
Functions
Management
device
■
Configured with a public
IP address.
■
Receiving management
commands from the
public network and
processing the received
commands
■
Providing management interfaces for all
switches in the cluster
■
Managing member devices by redirecting
commands
■
Forwarding commands to the intended
member devices
■
Neighbor discovery, topology information
collection, cluster management, cluster state
maintenance, and proxies
Member device
Normally, a member device
is not configured with a
public IP address.
■
Cluster member
■
Neighbor discovery, being managed by the
management device, running commands
forwarded by proxies, and failure/log
reporting.
Candidate device Normally, a candidate device
is not configured with a
public IP address.
A candidate device is a switch that does not
belong to any cluster, although it can be added
to a cluster.
Summary of Contents for 4200G 12-Port
Page 10: ...8 CONTENTS...
Page 14: ...4 ABOUT THIS GUIDE...
Page 46: ...32 CHAPTER 5 LOGGING IN THROUGH WEB BASED NETWORK MANAGEMENT SYSTEM...
Page 48: ...34 CHAPTER 6 LOGGING IN THROUGH NMS...
Page 60: ...46 CHAPTER 9 VLAN CONFIGURATION...
Page 64: ...50 CHAPTER 10 MANAGEMENT VLAN CONFIGURATION...
Page 80: ...66 CHAPTER 13 GVRP CONFIGURATION...
Page 98: ...84 CHAPTER 15 LINK AGGREGATION CONFIGURATION...
Page 112: ...98 CHAPTER 18 MAC ADDRESS TABLE MANAGEMENT...
Page 126: ...112 CHAPTER 19 LOGGING IN THROUGH TELNET...
Page 162: ...148 CHAPTER 20 MSTP CONFIGURATION...
Page 274: ...260 CHAPTER 29 IGMP SNOOPING CONFIGURATION...
Page 276: ...262 CHAPTER 30 ROUTING PORT JOIN TO MULTICAST GROUP CONFIGURATION...
Page 298: ...284 CHAPTER 33 SNMP CONFIGURATION...
Page 304: ...290 CHAPTER 34 RMON CONFIGURATION...
Page 338: ...324 CHAPTER 36 SSH TERMINAL SERVICES...
Page 356: ...342 CHAPTER 38 FTP AND TFTP CONFIGURATION...
Page 365: ...Information Center Configuration Example 351 S4200G terminal logging...
Page 366: ...352 CHAPTER 39 INFORMATION CENTER...
Page 378: ...364 CHAPTER 40 BOOTROM AND HOST SOFTWARE LOADING...
Page 384: ...370 CHAPTER 41 Basic System Configuration and Debugging...
Page 388: ...374 CHAPTER 43 NETWORK CONNECTIVITY TEST...
Page 406: ...392 CHAPTER 45 CONFIGURATION OF NEWLY ADDED CLUSTER FUNCTIONS...