Option 82 Supporting Configuration
397
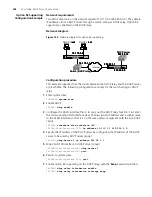
Configuring the dynamic user address entry updating function
When a DHCP client obtains an IP address from a DHCP server with the help of a
DHCP relay, the DHCP relay creates an entry (dynamic entry) in the user address table
to track the binding information about the IP address and MAC address of the DHCP
client. But as a DHCP relay does not process DHCP-RELEASE packets, which are sent
to DHCP servers by DHCP clients through unicast when the DHCP clients release IP
addresses, the user address entries maintained by the DHCP cannot be updated in
time. The dynamic user address entry updating function is developed to resolve this
problem.
The dynamic user address entry updating function works as follows: at regular
intervals, the DHCP relay sends a DHCP-REQUEST packet that carries the IP address
assigned to a DHCP client and its own MAC address to the corresponding DHCP
server. If the DHCP server answers with a DHCP-ACK packet, the IP address is
available (it can be assigned again) and the DHCP relay ages out the corresponding
entry in the user address table. If the DHCP server answers with a DHCP-NAK packet,
the IP address is still in use (the lease is not expired) and the DHCP relay remains the
corresponding user address entry unchanged.
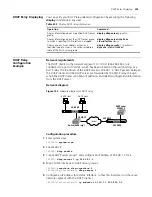
Option 82 Supporting
Configuration
Prerequisites
■
Before configuring option 82 supporting on a DHCP relay, make sure that the
DHCP relay is configured and operates properly.
■
The DHCP server operates properly. Address allocation policy-related
configurations (such as address pools and the lease time) are performed.
■
The routes between the DHCP relay and the DHCP server are reachable.
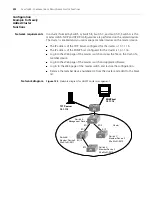
Enabling Option 82
Supporting on a DHCP
Relay
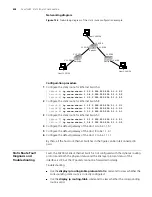
The following operations are expected to be performed on a DHCP relay-enabled
network device.
Table 341
Configure the dynamic user address entry updating function
Operation
Command
Description
Enter system view
system-view
—
Set the interval to
update DHCP user
address entries
dhcp-security
tracker
{
interval
|
auto }
Optional
By default, the update interval is automatically
determined by the number of DHCP user address
entries.
Table 342
Enable option 82 supporting on a DHCP relay
Operation
Command
Description
Enter system view
system-view
—
Enable option 82
supporting on the DHCP
relay
dhcp relay information
enable
Required
By default, this function is disabled.
Configure the strategy for
the DHCP relay to process
request packets
containing option 82
dhcp relay
information strategy
{
drop
|
keep
|
replace }
Optional
By default, the
replace
policy is adopted,
that is, the DHCP relay replaces the original
option 82 carried in a request packet with
its own option 82.
Summary of Contents for 4200G 12-Port
Page 10: ...8 CONTENTS...
Page 14: ...4 ABOUT THIS GUIDE...
Page 46: ...32 CHAPTER 5 LOGGING IN THROUGH WEB BASED NETWORK MANAGEMENT SYSTEM...
Page 48: ...34 CHAPTER 6 LOGGING IN THROUGH NMS...
Page 60: ...46 CHAPTER 9 VLAN CONFIGURATION...
Page 64: ...50 CHAPTER 10 MANAGEMENT VLAN CONFIGURATION...
Page 80: ...66 CHAPTER 13 GVRP CONFIGURATION...
Page 98: ...84 CHAPTER 15 LINK AGGREGATION CONFIGURATION...
Page 112: ...98 CHAPTER 18 MAC ADDRESS TABLE MANAGEMENT...
Page 126: ...112 CHAPTER 19 LOGGING IN THROUGH TELNET...
Page 162: ...148 CHAPTER 20 MSTP CONFIGURATION...
Page 274: ...260 CHAPTER 29 IGMP SNOOPING CONFIGURATION...
Page 276: ...262 CHAPTER 30 ROUTING PORT JOIN TO MULTICAST GROUP CONFIGURATION...
Page 298: ...284 CHAPTER 33 SNMP CONFIGURATION...
Page 304: ...290 CHAPTER 34 RMON CONFIGURATION...
Page 338: ...324 CHAPTER 36 SSH TERMINAL SERVICES...
Page 356: ...342 CHAPTER 38 FTP AND TFTP CONFIGURATION...
Page 365: ...Information Center Configuration Example 351 S4200G terminal logging...
Page 366: ...352 CHAPTER 39 INFORMATION CENTER...
Page 378: ...364 CHAPTER 40 BOOTROM AND HOST SOFTWARE LOADING...
Page 384: ...370 CHAPTER 41 Basic System Configuration and Debugging...
Page 388: ...374 CHAPTER 43 NETWORK CONNECTIVITY TEST...
Page 406: ...392 CHAPTER 45 CONFIGURATION OF NEWLY ADDED CLUSTER FUNCTIONS...