Chapter 10 Quality of Service (QoS)
XMG3512-B10A User’s Guide
135
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
10.4 The Queue Setup Screen
Click
Network Setting >
QoS > Queue Setup
to open the screen as shown next.
Use this screen to configure QoS queue assignment.
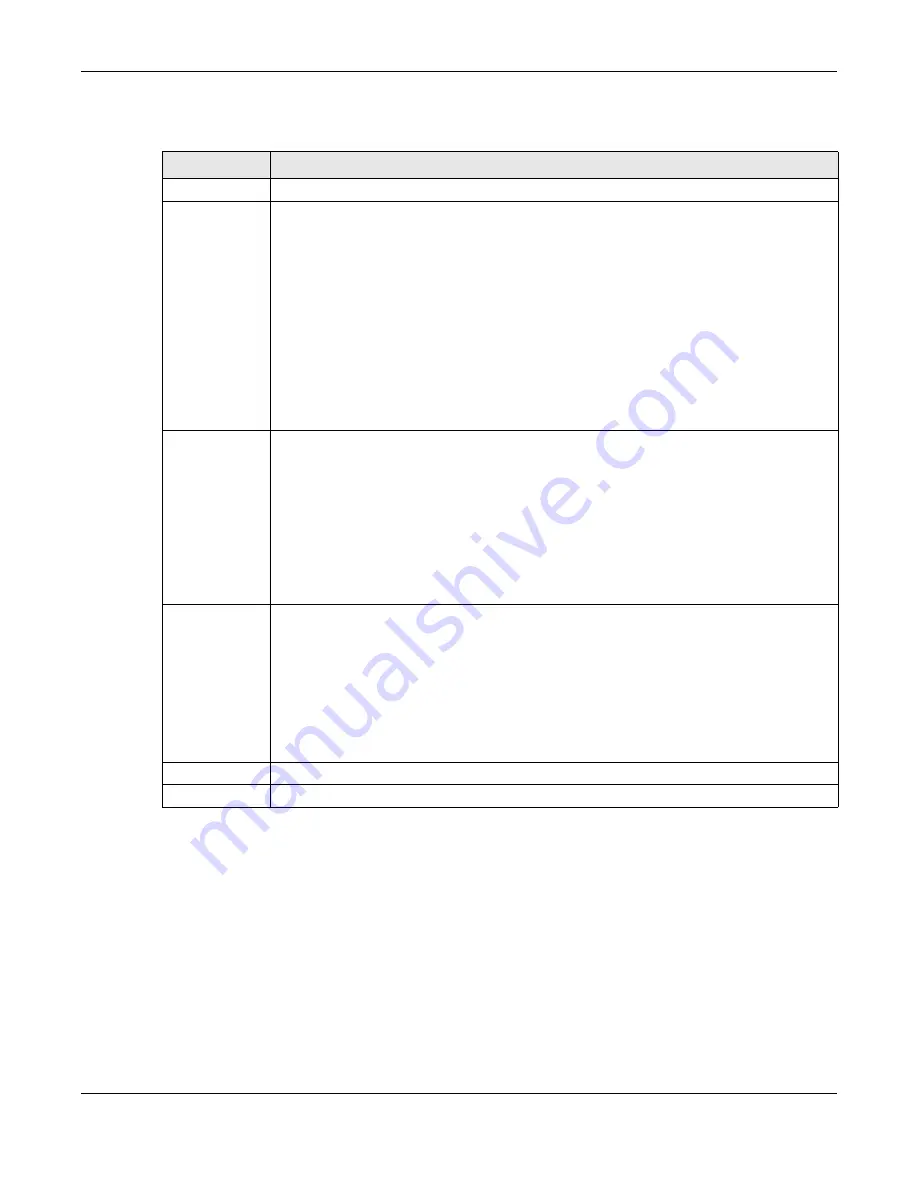
Table 44 Network Setting > QoS > General
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
QoS
Select the
Enable
check box to turn on QoS to improve your network performance.
WAN Managed
Upstream
Bandwidth
Enter the amount of upstream bandwidth for the WAN interfaces that you want to allocate using
QoS.
The recommendation is to set this speed to match the interfaces’ actual transmission speed. For
example, set the WAN interfaces’ speed to 100000 kbps if your Internet connection has an
upstream transmission speed of 100 Mbps.
You can set this number higher than the interfaces’ actual transmission speed. The XMG uses up
to 95% of the DSL port’s actual upstream transmission speed even if you set this number higher
than the DSL port’s actual transmission speed.
You can also set this number lower than the interfaces’ actual transmission speed. This will cause
the XMG to not use some of the interfaces’ available bandwidth.
If you leave this field blank, the XMG automatically sets this number to be 95% of the WAN
interfaces’ actual upstream transmission speed.
LAN Managed
Downstream
Bandwidth
Enter the amount of downstream bandwidth for the LAN interfaces (including WLAN) that you
want to allocate using QoS.
The recommendation is to set this speed to match the WAN interfaces’ actual transmission
speed. For example, set the LAN managed downstream bandwidth to 100000 kbps if you use a
100 Mbps wired Ethernet WAN connection.
You can also set this number lower than the WAN interfaces’ actual transmission speed. This will
cause the XMG to not use some of the interfaces’ available bandwidth.
If you leave this field blank, the XMG automatically sets this to the LAN interfaces’ maximum
supported connection speed.
Upstream Traffic
Priority Assigned
by
Select how the XMG assigns priorities to various upstream traffic flows.
•
None:
Disables auto priority mapping and has the XMG put packets into the queues
according to your classification rules. Traffic which does not match any of the classification
rules is mapped into the default queue with the lowest priority.
•
Ethernet Priority:
Automatically assign priority based on the IEEE 802.1p priority level.
•
IP Precedence:
Automatically assign priority based on the first three bits of the TOS field in the
IP header.
•
Packet Length:
Automatically assign priority based on the packet size. Smaller packets get
higher priority since control, signaling, VoIP, internet gaming, or other real-time packets are
usually small while larger packets are usually best effort data packets like file transfers.
Apply
Click
Apply
to save your changes.
Cancel
Click
Cancel
to restore your previously saved settings.
Содержание XMG3512-B10A
Страница 14: ...14 PART I User s Guide ...
Страница 23: ...Chapter 1 Introducing the XMG XMG3512 B10A User s Guide 23 Figure 8 Wall Mounting Example ...
Страница 33: ...Chapter 3 Quick Start XMG3512 B10A User s Guide 33 Figure 16 Quick Start Result Summary ...
Страница 56: ...56 PART II Technical Reference ...
Страница 139: ...Chapter 10 Quality of Service QoS XMG3512 B10A User s Guide 139 Figure 71 Classification Setup Add Edit ...
Страница 249: ...249 PART III Appendices Appendices contain general information Some information may not apply to your device ...
Страница 279: ...Appendix D Legal Information XMG3512 B10A User s Guide 279 Environmental Product Declaration ...






























